Figure 5.
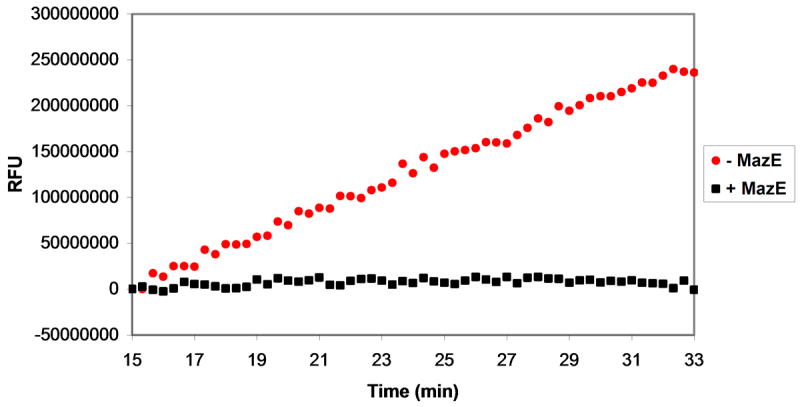
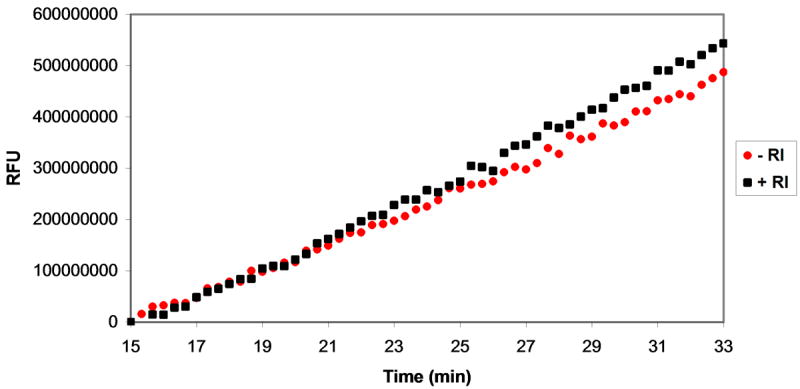
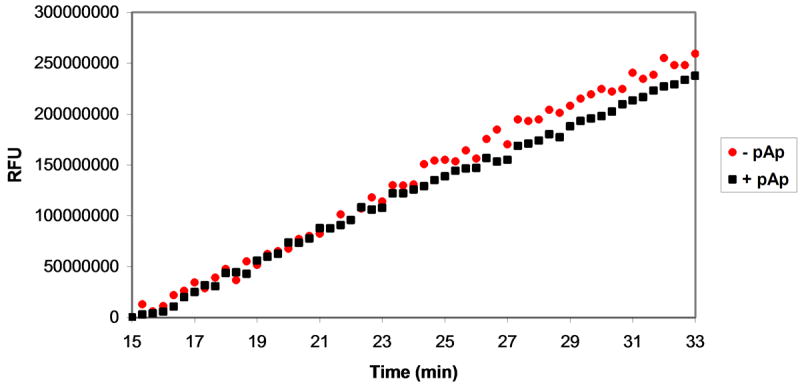
Assessment of MazF activity in the presence of ribonuclease inhibitors. Various ribonuclease inhibitors were added to MazF and elution buffer prior to their addition to oligonucleotide substrate. The effects of inhibitors on reaction velocity were monitored by fluorescence quantification by excitation at 485 nm and emission at 530 nm. A. A mixture of MazF and MazE was added to oligonucleotide substrate to final concentrations of 3 μM MazF and 1.5 μM MazE. Inhibition of MazF by MazE is indicated by the static fluorescence observed after MazF/MazE addition (black squares) in comparison to the increase in fluorescence observed after addition of MazF alone (red circles). B. A MazF/ribonuclease inhibitor (RI) solution was added to oligonucleotide substrate to final concentrations of 3 μM MazF and 200U RI. No inhibition of MazF by RI is observed as the fluorescence change of the oligonucleotide/MazF solution is the same in the presence and absence of RI. C. An experiment similar to that described in B was repeated for the RNaseA inhibitor, adenosine 3′,5′-diphosphate (pAp). Again, no inhibition of MazF by pAp is observed as the fluorescence change of the reaction solution is the same in the presence or absence of 1 mM pAp.
