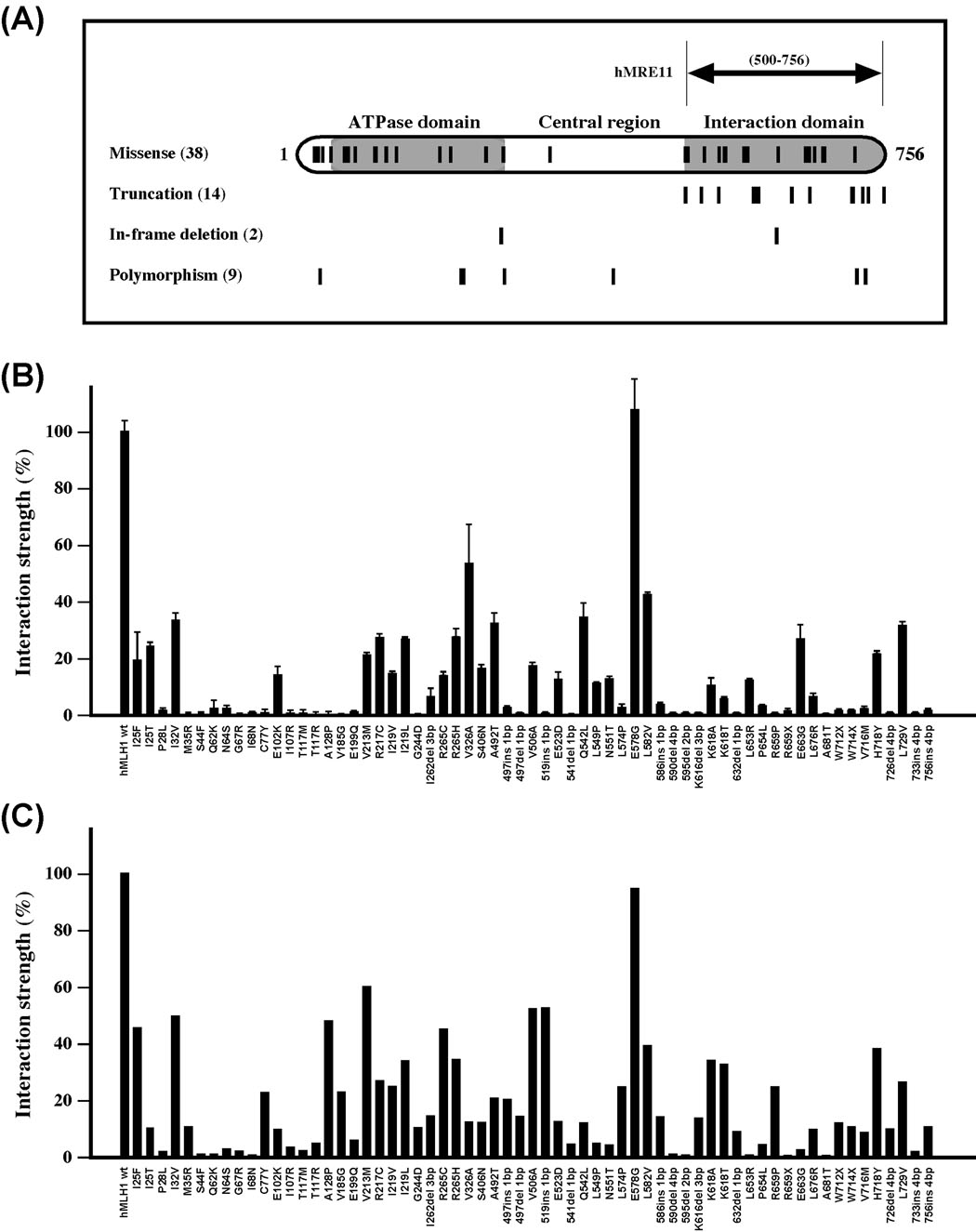
Figure 4.
Effects of hMLH1 mutations on hMLH1-hMRE11 interaction. (A) Schematic depiction of hMLH1 functional domains and the distribution of hMLH1 mutations analyzed in this study. The short vertical lines mark the locations of affected amino acid residues of 38 hMLH1 HNPCC missense mutations, as well as 14 truncations, 2 in-frame deletions, and 9 polymorphisms. (B) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of protein interactions. Relative interaction strength between hMRE11 and various mutant hMLH1 proteins were determined in reference to that of the wildtype control, and standard deviations (error bars) were calculated with three independent data points. (C) Far-Western blot analysis of the effects of hMLH1 mutations on the hMLH1-hMRE11 interaction. Membranes that were immobilized with purified hMRE11452–634 polypeptide were probed with crude lysate containing wildtype and various hMLH1 mutant proteins. Standard immunoblotting analysis was used to detect the captured hMLH1 proteins. Protein interactions between hMRE11 and various hMLH1 variants were normalized by comparison with that of the wildtype controls, in which the interaction between wildtype proteins was set to 100%.