Figure 1.
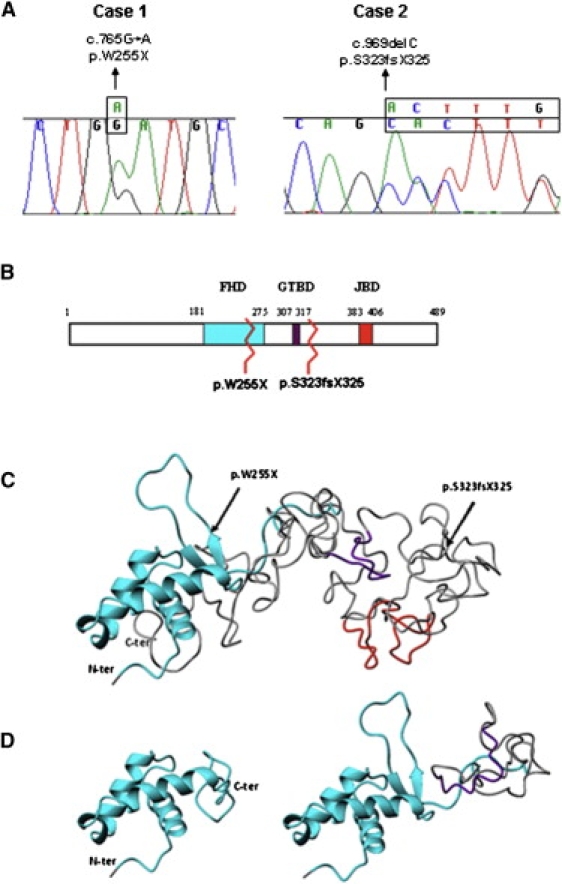
FOXG1 Mutations and Alterations of the Functional Domains
(A) Sequence tracing of FOXG1 mutations in the two patients. Mutated bases are indicated above the line.
(B) Schematic representation of FoxG1 protein. The three main functional domains are shown: the DNA binding fork-head domain in light blue (FHD), the Groucho-binding domain in violet (GTBD), and the JARID1B binding domain in red (JBD). The numbers at the top refer to the amino acid positions. Mutations are indicated by zigzag lines.
(C and D) Ribbon representation of the tertiary structure obtained with Phyre v.0.2 software. (C) shows the structure of the region containing the three functional domains of wild-type protein (amino acids 180–489). Arrows highlight the two mutations. The FHD domain (cyan) consists of three alpha helices and one beta hairpin (two beta strands and one loop), whereas the GTBD (violet) and JBD (red) domains are random coiled. (D) shows structural modification after p.W255X (left) and p.S323fsX325 (right) mutations. The p.W255X mutation determines a protein truncation just after the second beta strand leading to the loss of the beta hairpin and thus preventing DNA binding. The p.S323fsX325 mutation leaves the FHD domain intact and truncates the protein just after GTBD, inducing conformational changes that lead to its misfolding.
