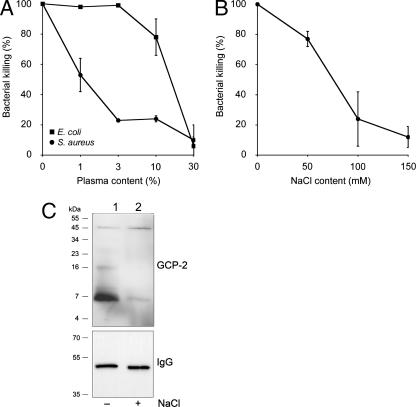
FIG. 5.
Effects of plasma and NaCl on the antibacterial activity of GCP-2/CXCL6, investigated by using a bactericidal assay (peptide concentration, 1 μM for 1 h at 37°C). (A) The presence of plasma at low concentrations strongly inhibited the killing of S. aureus, while plasma concentrations of 10% or higher were required to decrease the killing of E. coli. (B) S. aureus was chosen for examination of the effect of NaCl on the antibacterial activity of GCP-2/CXCL6. The antibacterial activity in this setup was greatly reduced in the presence of 100 and 150 mM NaCl. Data are means from three separate experiments. Error bars, standard errors of the means. (C) The ability of GCP-2/CXCL6 to interact with the bacterial membrane in the absence (lane 1) and presence (lane 2) of 150 mM NaCl was investigated. GCP-2/CXCL6 or IgG was adsorbed to S. aureus in the presence or absence of NaCl as indicated, followed by SDS-PAGE separation and Western blot analysis using anti-GCP-2 antibodies or protein G, respectively. Molecular mass is indicated on the left.