Fig. 8.
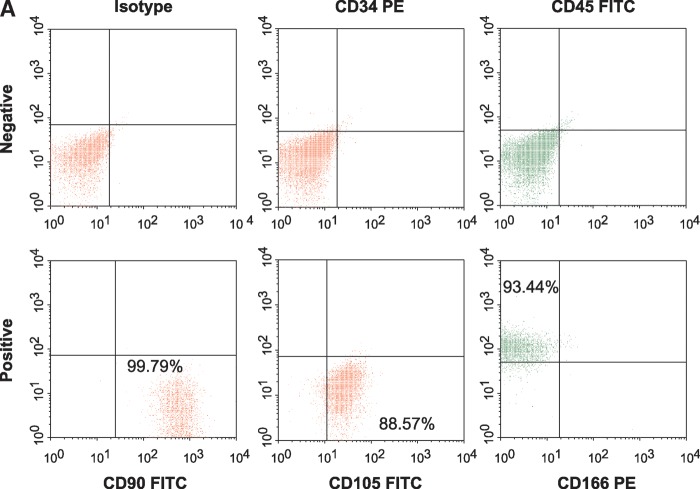
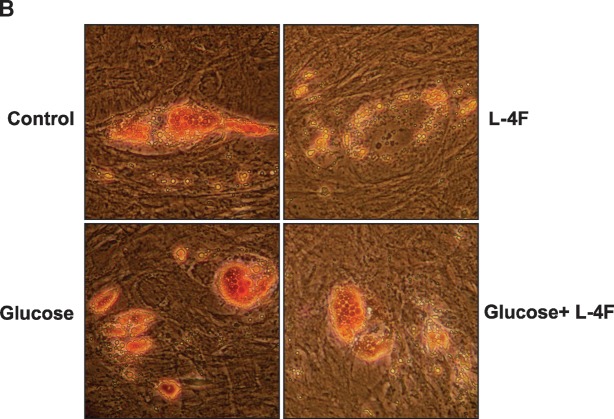
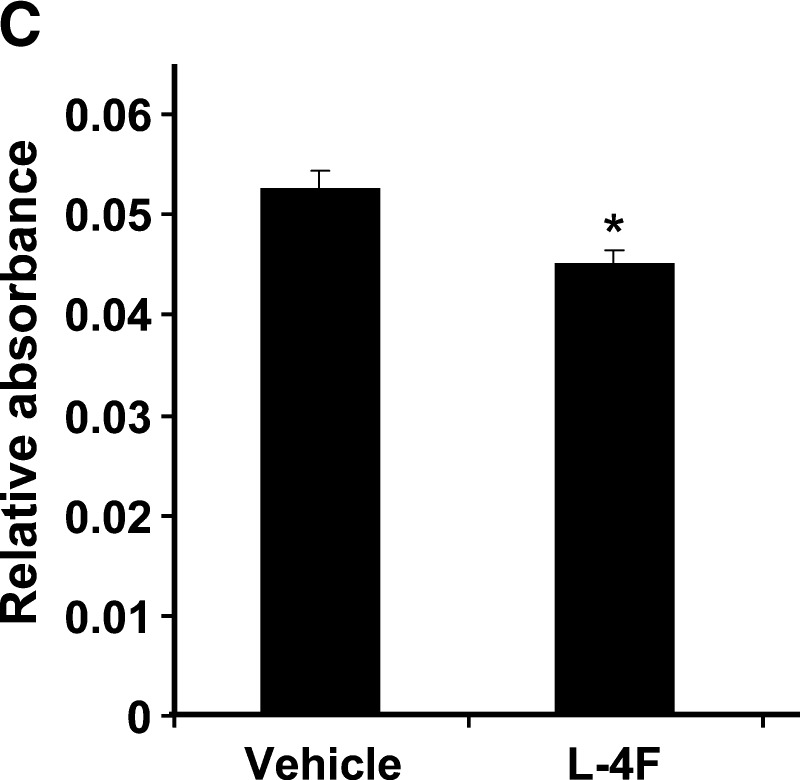
A: Surface expression of CD90, CD105, and CD166 on human MSCs (hMSCs) as determined by fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis. Percent of cells expressing positive markers CD90 (Thy-1), CD105 (endoglin and SH2), and CD166 (ALCAM, activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule) were 99.8%, 88.6%, and 93.4%, respectively. CD45 (common lymphocytes antigen) and CD34 (hematopoietic stem cell marker) were used as negative markers. CD45 and CD34 were expressed in less than 0.2% of cells, the same as unstained isotypes. B, C: Effect of L-4F on human MSC-derived adipogenesis. B: Oil Red O staining of hMSC cultures 10 days after induction of conditions favoring adipogenesis. Human MSCs were cultured in the presence and absence of high glucose and in the presence and absence of L-4F (20 μg/ml) and subjected to Oil Red O staining as described in Materials and Methods. C: Oil Red O stain was extracted and quantified by relative absorbance as described in Materials and Methods, confirming that L-4F treatment significantly reduced adipogenesis. The values shown are the mean ± SEM, n = 6; *P < 0.022 vehicle-treated hMSC versus L-4F-treated hMSC.