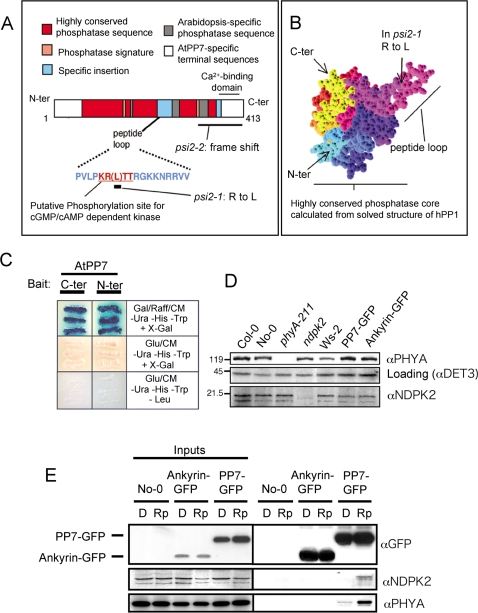
Figure 3. Structure of the AtPP7 protein and screen for AtPP7 interacting protein.
(A) Location of EMS point mutations on the protein sequence and description of the conserved and non-conserved phosphatase domains. (B) Location of the peptide loop domain in the periphery of the main phosphatase core, as calculated from the highly similar domain of hPP1 using Geno3D [56]. (C) Yeast colonies positive in a yeast two-hybrid assay using the N- and C-terminus of AtPP7 as bait and an Arabidopsis cDNA library as preys. Both AtPP7 termini interact with a fragment of the Arabidopsis nucleotide diphosphate kinase 2 (NDPK2) protein. (D) Level of NDPK2 and phyA protein in ndpk2 and phyA null mutant lines and their related wild types grown 4 days in darkness at 22°C. Western blot analysis were performed as described in text. (E) NDPK2 and phyA interacts with AtPP7 in vivo. Transgenic Arabidopsis expressing either a AtPP7-GFP fusion or a constitutive nuclear ankyrin-GFP fusion were grown 4 days in darkness and exposed to a 5 min pulse of red light 10 µmol m−2 s−1 at 22°C (D: dark control; Rp: red pulse). Protein extracts from these plants were incubated with agarose-bound anti-GFP antibodies. Co-immunoprecipitated NDPK2, phyA and DET3 were then detected after SDS-PAGE separation on nitrocellulose-blotted gel using specific antibodies. Input samples contained total protein extract.