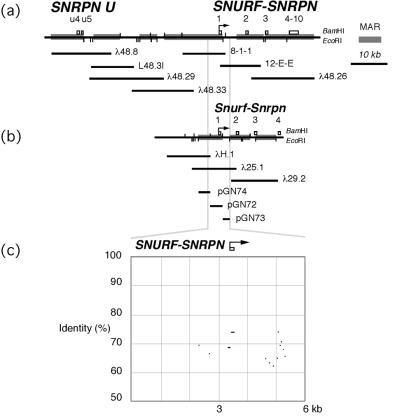
Figure 2.
A summary of the results of NMBAs for (a) the human 15q11-q13 IC/SNURF-SNRPN region and (b) the mouse Snurf-Snrpn locus. Exons 1–10 of the SNURF-SNRPN gene (13) and two exons of the SNRPN U transcript (11, 15) are shown. NMBAs were performed on each of the genomic clones shown (primary data in www.pnas.org). The gray bars on the human and mouse maps show the extent of MARs identified. (a) In total, 49.1 kb of the 68.9-kb region at the human IC/SNURF-SNRPN gene region are biochemically defined as MARs by using the NMBA. (b) The organization of MARs at the homologous mouse region is similar in terms of the density and distribution of MARs. (c) Sequence comparison [percent identity plots (31)] reveals extensive divergence of sequence at these loci, except at the immediate promoter/exon 1 region of SNURF-SNRPN/Snurf-Snrpn and within intron 1. Conservation of MARs is therefore not accounted for by identity of sequence between these two species.