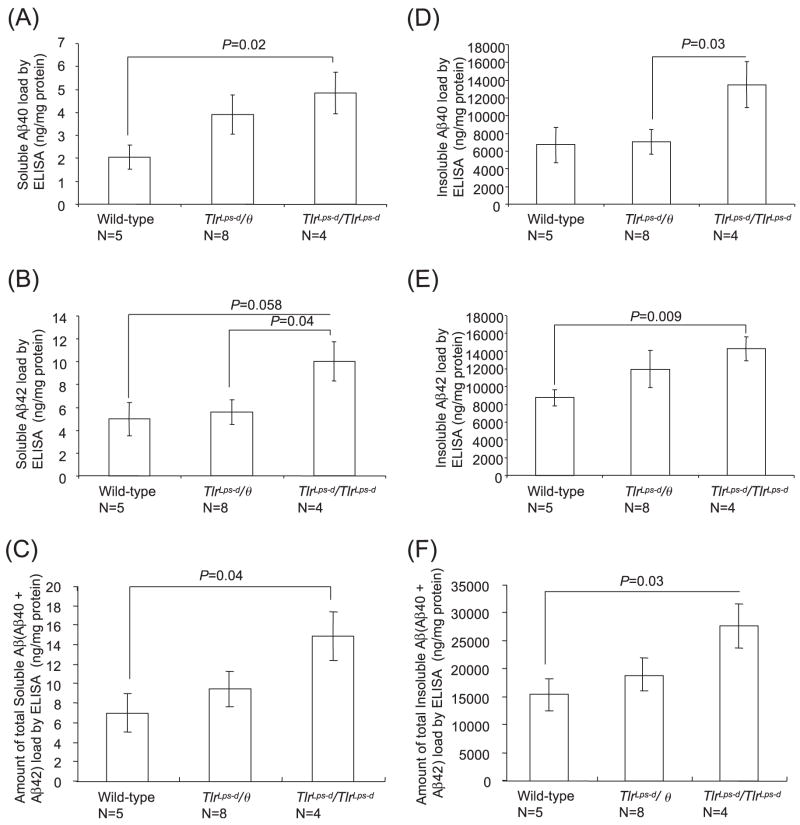
Fig. 4.
Quantification of buffer-soluble and insoluble Aβ in the cerebrum by the Aβ40- and Aβ42-specific ELISA. The cerebral buffer-soluble Aβ40 content in TlrLps-d/TlrLps-d mice is higher than that in TLR4 wild-type mice (A). The cerebral buffer-soluble Aβ42 content in TlrLps-d/TlrLps-d mice is higher than that in TlrLps-d/θ mice (B). The amount of total buffer-soluble Aβ (Aβ40 + Aβ42) is higher than that in TLR4 wild-type mice (C). The cerebral insoluble Aβ40 content in TlrLps-d/TlrLps-d mice is higher than that in TlrLps-d/θ mice (D). The cerebral insoluble Aβ42 content in TlrLps-d/TlrLps-d mice is higher than that in TLR4 wild-type mice (E). The amount of total insoluble Aβ (Aβ40 + Aβ42) in TlrLps-d/TlrLps-d mice is higher than that in TLR4 wild-type mice (F).