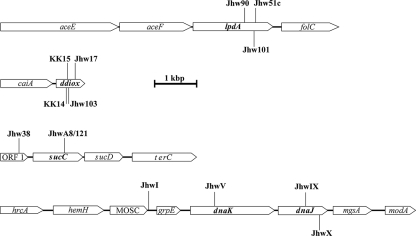
FIG. 3.
Tn5::mob insertions in the genome of T. mimigardefordensis strain DPN7 and identification of genes adjacent to the insertion loci. The diagrams show the localization of Tn5::mob insertions in four regions of the T. mimigardefordensis strain DPN7 genome in the 13 independent mutants showing fully or partially impaired growth on DTDP. The positions of Tn5::mob insertions in the respective mutants (mutant codes are given in Table 2) are indicated. Lengths and directions of arrows showing the genes indicate the proportional lengths and directions of transcription, respectively, of the corresponding genes. Putative identities of the gene products suggested from the amino acid sequence identities to proteins in the GenBank database are as follows: aceE, pyruvate dehydrogenase; aceF, dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase; lpdA, dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase; folC, folylpolyglutamate synthase/dihydrofolate synthase; ddiox, thiol dioxygenase; caiA, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; ORF1, no sequence similarities; sucC, succinyl-CoA synthetase, beta chain; sucD, succinyl-CoA synthetase, alpha chain; terC, tellurium resistance protein; hrcA, heat-inducible transcription repressor; hemH, ferrochelatase; MOSC, molybdenum cofactor sulfurase, C-terminal end; grpE, nucleotide exchange factor; dnaK, Hsp70-like chaperone; dnaJ, molecular chaperone; mgsA, methylglyoxal synthase; and modA, molybdate binding protein. Bar, 1,000 base pairs.