TABLE 5.
Prediction of ethanol titers of TCS083/pLOI297 and CT1101/pLOI297a
| Strain | Substrate(s) | Titer of biomass (g/liter) | w1c (%) | w2c (%) | Predicted amt of ethanolb (g/liter) | Amt of ethanol measured (g/liter) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCS083/pLOI297 | Glucose | 3.11 ± 0.47 | 16 ± 2 | 84 ± 2 | 39.20 ± 0.34 | 38.77 ± 0.63 |
| TCS083/pLOI297 | Xylose | 3.25 ± 0.12 | 42 ± 1 | 58 ± 1 | 39.22 ± 0.09 | 39.07 ± 0.59 |
| TCS083/pLOI297 | Glucose and xylose | 3.54 ± 0.16 | 32 ± 1 | 68 ± 1 | 39.46 ± 0.57 | 38.81 ± 0.91 |
| CT1101/pLOI297 | Glucose and xylose | 1.48 ± 0.02 | 39 ± 1 | 61 ± 1 | 19.32 ± 0.73 | 20.03 ± 0.18 |
Predictions are based on the overall stoichiometric equations of the efficient ethanol-producing pathways (Table 1). The values are reported as means ± standard deviations of six independent measurements from duplicate runs of batch bioreactors.
The predicted amount of ethanol can be calculated as follows: 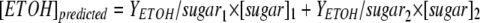 , where [ETOH]predicted (g/liter) is the ethanol titer predicted, [sugar] (g/g) is the amount of sugar consumed, and YETOH/sugar (g ethanol/g sugar) is the theoretical yield of ethanol on sugar calculated by using stoichiometric equations. Subscripts “1” and “2” refer to the growth-associated phase and non-growth-associated phase, respectively.
, where [ETOH]predicted (g/liter) is the ethanol titer predicted, [sugar] (g/g) is the amount of sugar consumed, and YETOH/sugar (g ethanol/g sugar) is the theoretical yield of ethanol on sugar calculated by using stoichiometric equations. Subscripts “1” and “2” refer to the growth-associated phase and non-growth-associated phase, respectively.
w1 and w2 are the weighting factors of glucose (xylose) channeled into either the growth-associated ethanol-producing pathway or the non-growth-associated ethanol-producing pathway, respectively. w1 can be calculated as follows: w1 = 100% × [sugar]1/[sugar], and w2 = 100% − w1. [sugar]1 can be determined by the following formula: 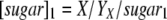 , where X (g/liter) is the experimentally determined biomass and
, where X (g/liter) is the experimentally determined biomass and 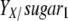 (g biomass/g sugar) is the yield of biomass on sugar calculated by using stoichiometric equations.
(g biomass/g sugar) is the yield of biomass on sugar calculated by using stoichiometric equations.
