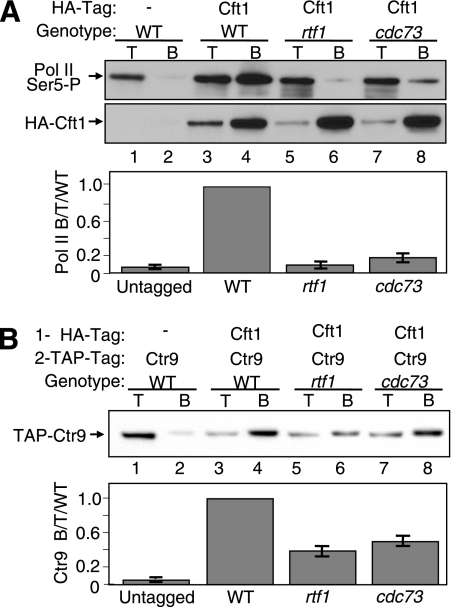
FIG. 5.
Dissociation of the Paf1C from Pol II reduces the association of polyadenylation factor Cft1 with Pol II and reveals a direct association between the Paf1C and Cft1. Extracts from strains bearing the indicated tagged proteins and mutations were immunoprecipitated with α-HA antibody and then probed with appropriate antibodies. Signals in the lower panels were quantitated as described in Materials and Methods as the ratio of Pol II bound to total protein-, and the results are expressed relative to the WT ratio, which was set at 1. T, 10 μg of total protein; B, bound IP pellet; −, absence of HA-tagged Cft1. (A) The loss of Rtf1 or Cdc73 reduces the association of Cft1 with Pol II. HA-tagged Cft1 was immunoprecipitated, and the presence of the Ser5-P CTD form of Pol II was detected with the α-Ser5-P CTD H14 antibody (upper panel). The protein blot was stripped and reprobed with α-HA for the presence of HA-tagged Cft1 (middle panel). The error bars in the graph in the lower panel represent the standard deviations of data from four repetitions of the experiment. The strains used were YJJ1824 (lanes 1 and 2), YJJ1864 (lanes 3 and 4), YJJ1849 (lanes 5 and 6), and YJJ1850 (lanes 7 and 8). (B) The Paf1C and Cft1 interact in the absence of Rtf1 or Cdc73. HA-tagged Cft1 was immunoprecipitated, and the presence of coimmunoprecipitated TAP-tagged Ctr9 was detected with α-TAP (upper panel). The solid bars representing quantitated data in the lower panel indicate the averages and the error bars show the ranges of results obtained from replicate experiments. The strains used were YJJ1824 (lanes 1 and 2), YJJ1864 (lanes 3 and 4), YJJ1849 (lanes 5 and 6), and YJJ1850 (lanes 7 and 8).