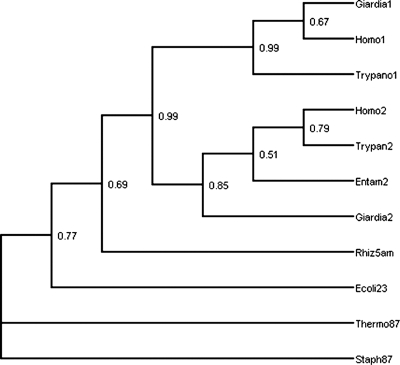
FIG. 7.
Phylogenetic analyses of gSPTs. The tree is a majority rule consensus tree constructed from 100 bootstrap replicates of maximum likelihood phylogenies for gspt-1 and gspt-2 sequences, along with homologous aminoacyl transferase sequences. The individual trees were constructed on the assumption of a Jones-Taylor symmetric amino acid substitution model. The taxon and sequence abbreviations are as follows: Giardia1 and Giardia2, gSPT-1 and gSPT-2, respectively; Entam2, SPT-2 from Entamoeba histolytica (lacking SPT-1); Trypano1 and Trypan2, Trypanosoma cruzi; Homo1 and Homo2, Homo sapiens. For aminoacyl transferases, the suffix “5am” indicates 5-amino leuvulinic acid synthase, “87” indicates 8-amino-7-oxononanoate synthase, and “23” indicates 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate coenzyme, and the archaeal and eubacterial taxa included are Thermophilus aquaticus (Therm), Staphylococcus aureus (Staph), Escherichia coli (Ecoli), and Rhizobium leguminosarum (Rhiz).