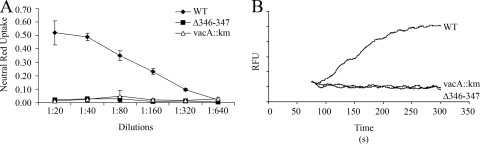
FIG. 2.
Functional analysis of VacA Δ346-347 activity. H. pylori strains expressing wild-type VacA or VacA Δ346-347, and a vacA-null mutant strain (60190 vacA::km) were grown in broth culture, and VacA proteins were purified as described in Materials and Methods. Concentrations of wild-type VacA and VacA Δ346-347 were normalized based on immunoblot assays, and the preparations were tested for vacuolating activity and membrane depolarization. (A) Analysis of vacuolating activity. For VacA-containing samples, a dilution of 1:20 corresponds to a VacA concentration of approximately 15 μg/ml. An equivalent volume of sample from the vacA::km-null mutant strain was tested as a control. Acid-activated samples were added to the medium overlying HeLa cells and vacuolating activity was quantified by using a neutral red uptake assay. The results represent the mean ± the SD from triplicate samples. (B) Analysis of depolarization. AZ-521 cells were loaded with oxonol VI (a probe used to monitor membrane potential). After the addition of acid-activated VacA proteins (10 μg/ml) or a control preparation (vacA::km), changes in fluorescence were monitored. Wild-type VacA induced membrane depolarization, whereas VacA Δ346-347 and the control vacA::km preparation did not. RFU, relative fluorescence units. The results are representative of four experiments. WT, wild type.