FIG. 4.
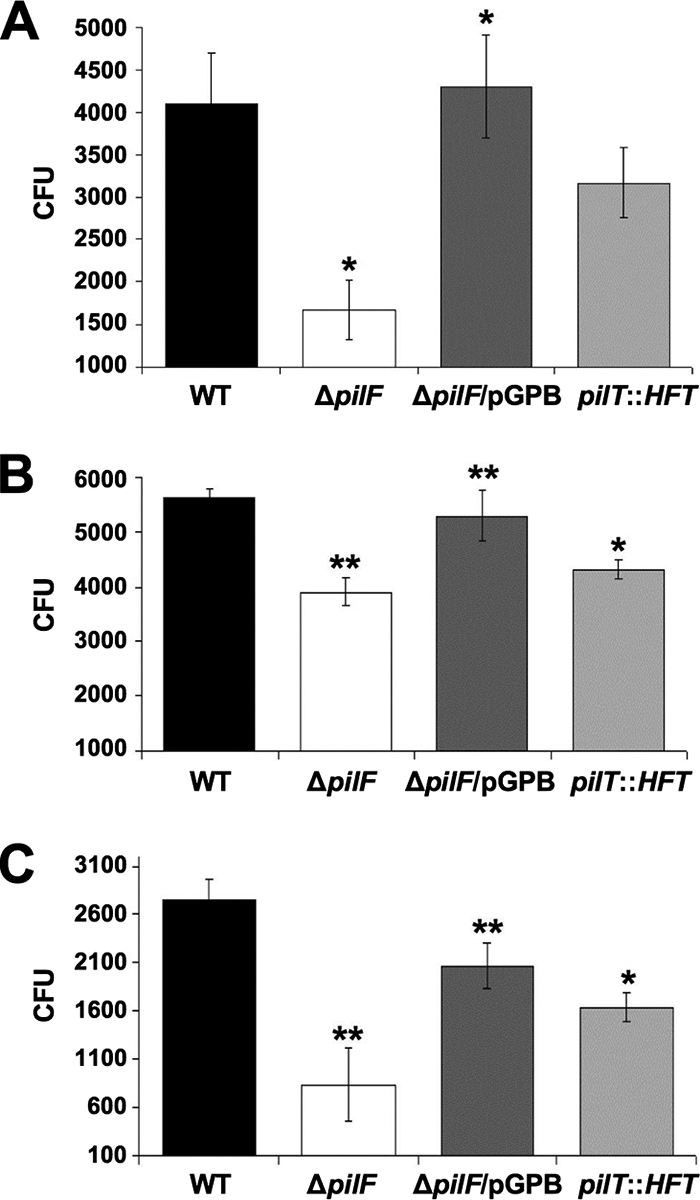
pilF and pilT contribute to host cell adherence. Cells were treated with cytochalasin D to inhibit the internalization of bacteria and then infected with wild-type LVS (WT), DTLB (ΔpilF), DTLB complemented with pilF (ΔpilF/pGPB), or the pilT::HimarFT mutant. The graphs show the CFU of bacteria that adhered to murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (A), A549 human lung epithelial cells (B), and FL83B murine hepatocytes (C). Error bars indicate the standard deviation of triplicate samples. P values were calculated by using a paired t test, comparing DTLB or pilT:HimarFT with the wild-type LVS or comparing DTLB/pGPB with DTLB (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.02).
