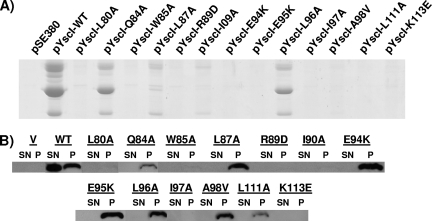
FIG. 5.
Conserved residues in the C terminus of YscI are critical for T3SS function. (A) Yop secretion by YscI mutants. Mutations in yscI were introduced in trans into the yscI null strain SAL4. Bacteria were grown in Yop-inducing medium (BHI minus calcium), and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. Secreted supernatant fractions were isolated by centrifugation, precipitated with TCA, and run on SDS-PAGE gels. Yops were visualized by staining with Coomassie blue. Higher induction levels did not result in greater Yop secretion (data not shown). pSE380, vector control; pYscI-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscI; pYscI-L80A to pYscI-K113E, plasmids expressing YscI proteins with the indicated mutations. (B) YscI expression and secretion. The aforementioned strains were grown as described above. Secreted supernatant (SN) and cell pellet (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation, and proteins in the supernatant were TCA precipitated. Equal percentages of the two fractions were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and YscI was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. Proteins are indicated by the corresponding mutations. V, vector control; WT, wild type.