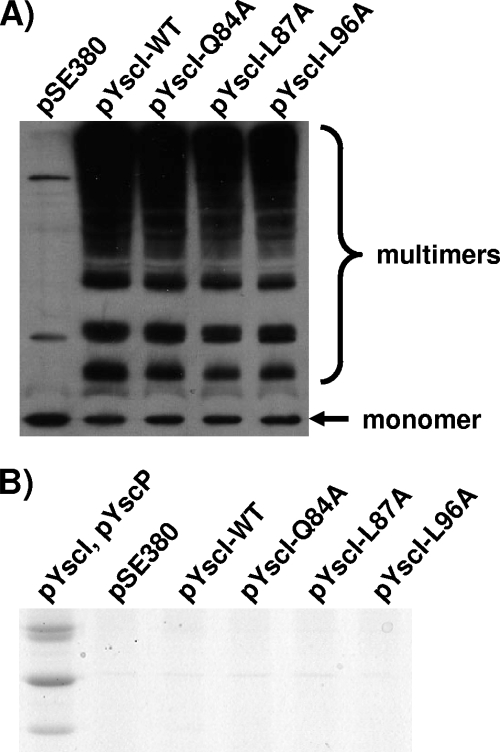
FIG. 9.
The YscI Q84A, L87A, and L96A mutant forms assemble needles in the absence of YscP. (A) Either wild-type YscI or the indicated YscI mutant forms were expressed in trans in the yscI yscP double null strain SAL6. Bacteria were grown in BHI-minus-calcium medium, and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. Surface proteins were cross-linked via the addition of 2.5 mM BS3. Samples were run on SDS-PAGE gels, and the needle component YscF was detected by Western blotting using a polyclonal antiserum. pSE380, vector control; pYscI-WT, plasmid expressing wild-type YscI; pYscI-Q84A to pYscI-L96A, plasmids expressing YscI proteins with the indicated mutations. (B) The aforementioned strains were grown in Yop-inducing medium (BHI minus calcium), and YscI expression was induced with 20 μM IPTG. In addition, a control strain expressing YscI and YscP from two compatible plasmids (pYscI and pYscP) was utilized; YscI expression was induced as described above, and YscP expression was induced with 0.2% arabinose. Secreted supernatant fractions were isolated by centrifugation, precipitated with TCA, and run on SDS-PAGE gels. Yops were visualized by staining with Coomassie blue.