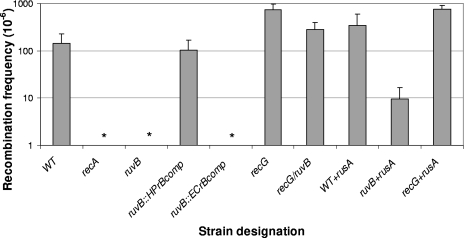
FIG. 2.
Intergenomic recombination frequencies of H. pylori wild-type, mutant, and complemented strains. H. pylori strains were transformed to streptomycin resistance with an 800-bp A128G rpsL PCR product (23); bars represent means ± standard deviations of transformation frequency. The strains transformed were H. pylori JP26 (wild type [WT]) and isogenic recA, recG, ruvB, and recG ruvB mutants, an ruvB mutant complemented with either H. pylori ruvB (JP26 HPruvBcomb), or E. coli ruvB (JP26 ECruvBcomp) downstream of a strong (ureA) promoter, and H. pylori wild-type and recG and ruvB mutant strains expressing RusA (JP26 WT+RusA, JP26 recG+rusA, and JP26 ruvB+rusA, respectively). As expected, no transformants were observed in the recA mutant control. The recG::cat strain exhibits a significantly higher transformation frequency than the wild type (P < 0.05). Asterisks indicate that no transformants were detected for the recA, ruvB, and ECruvBcomp mutants (frequency, <10−8). Complementation with H. pylori but not E. coli ruvB restored transformation. Addition of RusA to either the wild type or ruvB mutants enhanced resistance but had no effect in the recG mutant.