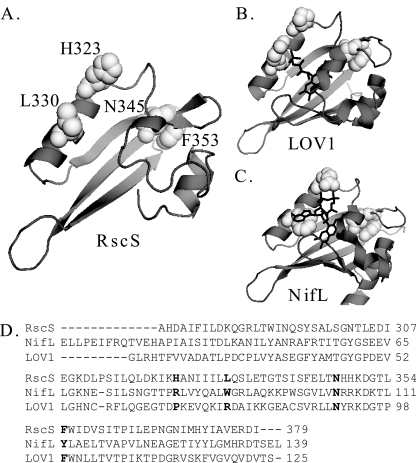
FIG. 6.
RscS PAS domain. (A) RscS PAS domain sequence threaded onto the LOV1 domain of the Phot1 protein of C. reinhardtii (1N9L) (2, 14; http://swissmodel.expasy.org//). Residues subjected to mutagenesis in this study are shown in white spacefill and are labeled. (B) LOV1 domain of the Phot1 protein of C. reinhardtii (1N9L) (14). The FMN cofactor is indicated by black lines. Residues corresponding to the residues mutagenized in RscS are shown in white spacefill. (C) A. vinelandii NifL PAS domain structure (2GJ3) (24). The FAD cofactor is indicated by black lines. Residues corresponding to the residues mutagenized in RscS are shown in white spacefill. (D) Sequence alignment for the putative PAS domain of RscS, the A. vinelandii NifL PAS domain, and the LOV1 domain of the Phot1 protein of C. reinhardtii. Residues targeted for substitution in RscS and the corresponding residues in NifL and LOV1 are indicated by bold type. Crystal structures were visualized using the PyMOL molecular graphics system (http://www.pymol.org).