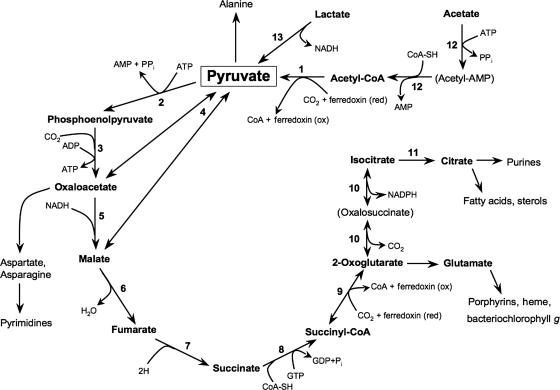
FIG. 2.
Putative pathway of carbon metabolism in H. modesticaldum (adapted from reference 44). A partial reverse citric acid cycle with CO2 incorporation via PEP carboxykinase is shown. The enzymes involved in the reduction of acetate to pyruvate putatively function in an oxidative direction during chemotrophic (dark) growth on pyruvate. The oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA is likely accompanied by hydrogen evolution via an [FeFe] hydrogenase. The numbers indicate the following enzymes: 1, pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; 2, pyruvate-phosphate dikinase; 3, PEP carboxykinase; 4, oxaloacetate decarboxylase; 5, malate dehydrogenase; 6, fumarase; 7, fumarate reductase; 8, succinyl-CoA synthetase; 9, 2-oxoglutarate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase; 10, NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase; 11, aconitate hydratase; 12, AMP-forming acetyl-CoA synthetase; 13, lactate dehydrogenase.