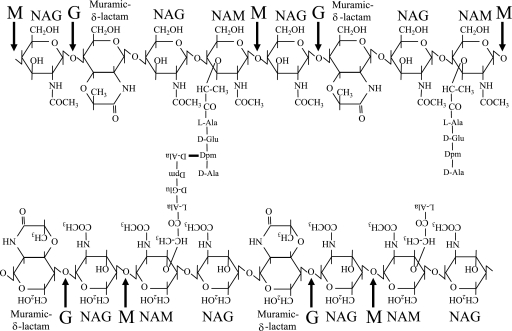
FIG. 1.
Spore PG structure and hydrolysis. Spore PG structure is well conserved across bacilli and clostridia (2, 3, 5, 23, 28, 30). The glycan strands contain alternating NAG and NAM residues in which approximately every second muramic acid residue is converted to muramic-δ-lactam. Approximately 26% of muramic acid residues have tetrapeptide side chains, 20% have l-alanine side chains, and a small percentage carry tripeptides. The peptides are utilized in cross-linking the glycan strands. Arrows indicate the cleavage sites of the muramidase mutanolysin (M) and of a glucosaminidase (G) active during germination. The actions of these enzymes singly produce tetrasaccharide and together produce trisaccharide muropeptides. The presence of adjacent muramic-δ-lactam residues results in the production of hexasaccharide and pentasaccharide muropeptides.