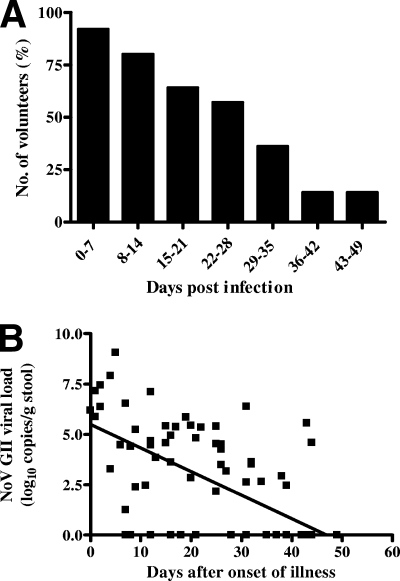
FIG. 2.
(A) The percentages of volunteers positive for the detection of NoV GII RNA in stool specimens over time. The median duration of viral excretion was 28.5 days (n = 14 volunteers, range of 13.5 to 44.5 days, mean of 28.7 days). The initial day of illness equaled day 0. (B) Rate of viral decay in NoV GII-infected volunteers. NoV GII RNA was quantified in all 14 volunteers from the onset of gastrointestinal illness until the second consecutive negative NoV GII RNA specimen. Assuming an exponential decay of viral load over time, the following equation was determined: V = V010−dt, where d is the viral decay rate (day−1), V is NoV GII RNA copies/g at time t (day), and V0 is the initial viral load. The rate of viral decay was obtained by fitting the above equation on a logarithmic (log10) scale (r2 = 0.4236, P < 0.0001), with the assumption that a measured viral load of 0.00 copies/g stool (defined as a cycle threshold value below the detection limit of the assay) was equivalent to 1 copy/g stool. The viral decay rate in NoV-infected individuals was 0.76 per day, which corresponds to a half-life (t1/2) of 2.5 days.