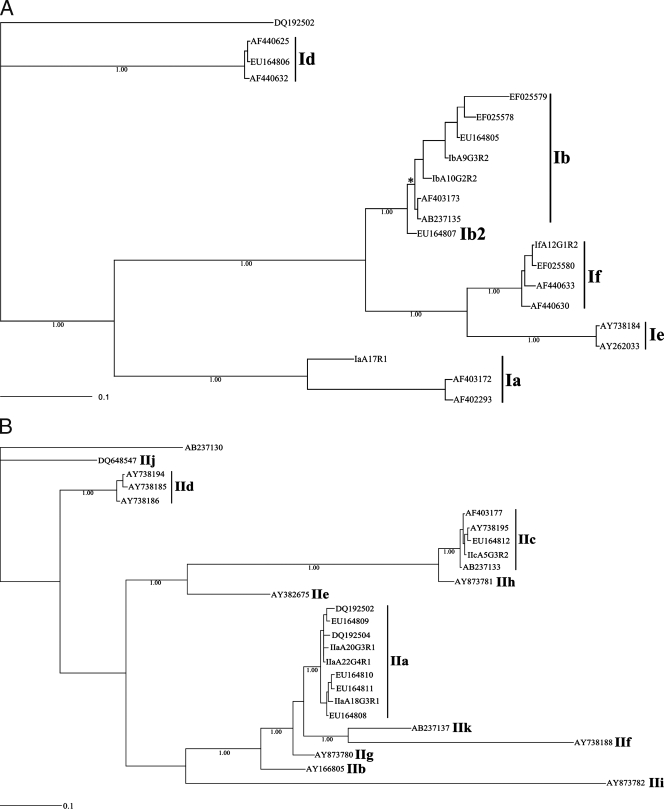
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of p-gp60 sequence data representing Cryptosporidium hominis (A) and C. parvum (B) from 62 human patients from Adelaide and surrounding areas of South Australia using key published sequence data for comparative purposes (1, 18, 40, 58, 71-73). From the present study, sequences representing C. hominis subgenotypes IaA17R1, IbA9G3R2, IbA10G2R2, and IfA12G1R2 have been deposited under accession numbers EU379544, EU379545, EU379546, and EU379547, respectively; those representing C. parvum subgenotypes IIaA18G3R1, IIaA20G3R1, IIaA22G4R1, and IIcA5G3R2 are available under accession numbers EU379548, EU379549, EU379550, and EU379551, respectively. The accession numbers of other (reference) sequences are indicated in the trees. Numbers beneath the node of each clade represent bootstrap support obtained using Bayesian inference; the bar indicates distance (0.1 substitutions per site). An asterisk indicates a pp of 1.00.