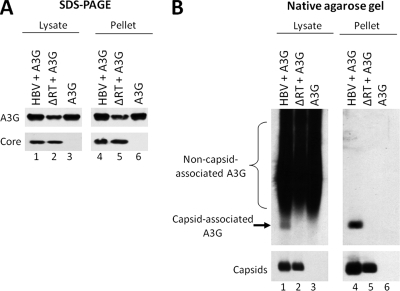
FIG. 1.
Native agarose gel electrophoresis assay as a reliable method for determining A3G incorporation into HBV nucleocapsids. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing either wild-type HBV or a polymerase-deficient HBV mutant (ΔRT) along with A3G. Cell lysates were prepared 72 h after transfection and subjected to ultracentrifugation over a sucrose gradient to separate HBV capsids from most cellular proteins. The unfractionated lysates (lanes 1 to 3) and the resuspended pellets (lanes 4 to 6) were loaded onto an SDS-PAGE gel (A) and a native agarose gel (B). Western blot analysis was used to detect the levels of HBV core protein (A, bottom panel), capsid (B, bottom panel), or A3G protein (A and B, upper panels). For native agarose gel analysis (B), A3G was detected by immunoblotting with the anti-A3G antibodies (B, upper panel), followed by subsequent reprobing of the same membrane for HBV capsids using the anti-HBV core protein antibody (B, bottom panel).