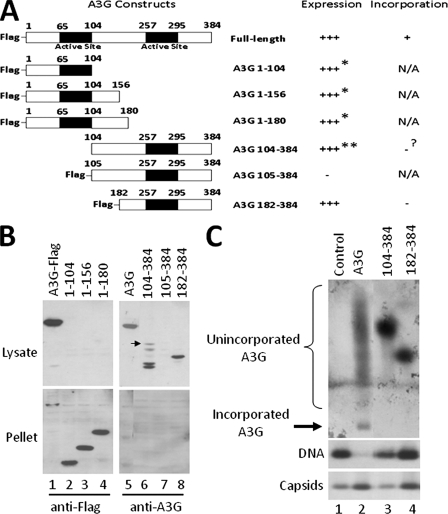
FIG. 7.
Requirement for the A3G N-terminal domain in encapsidation. (A) Schematic representation of the A3G deletion mutants and their expression and incorporation. All deletion constructs contain a Flag tag at the amino terminus of the protein, with the exception of A3G 104-384. (B and C) HepG2 cells were transfected with a plasmid expressing either the full-length A3G or the A3G deletion mutants together with the HBV plasmid. Seventy-two hours posttransfection, cells were lysed in NP-40 and total A3G levels in the lysate (soluble) and pellet (insoluble) (B) and the amount of packaged A3G (C) were determined by SDS-PAGE and native agarose gel assay, respectively. Expression of C-terminal A3G fragments and incorporated A3G levels were detected using anti-A3G antibody, while N-terminal A3G fragments were detected by using anti-Flag antibody. For the native agarose gel analysis (C), A3G was detected by immunoblotting with anti-A3G antibodies (B, upper panel), followed by reprobing of the same membrane for HBV capsids using the anti-HBV core antibody (B, bottom panel). *, protein expressed but insoluble; **, protein expressed but partially degraded; ?, incorporation status uncertain due to protein degradation. The arrow in panel B indicates the intact A3G 104-384 protein.