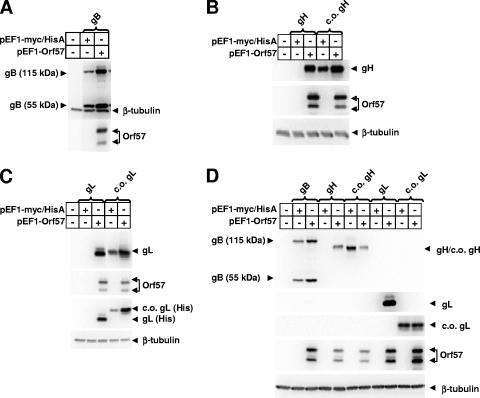
FIG. 1.
Achievement of gH and gL expression by codon optimization or by coexpression of ORF57. RRV gH, gL, and gB gene coding regions were cloned in-frame into the pEF1-myc/HisA expression vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) after PCR amplification from the RRV26-95 cosmid library (1). RRV ORF57 was PCR amplified from the RRV26-95 cosmid library and inserted in-frame into the pEF1-V5/His expression vector (Invitrogen). Codon-optimized versions of RRV gH and gHt were PCR amplified from a template plasmid acquired through DNA2.0 (Menlo Park, CA) and inserted into the pEF1-myc/HisA expression vector. A codon-optimized version of RRV gL was PCR amplified from a template plasmid acquired through DNA2.0 and inserted into the pEF1-V5/HisA expression vector. Recloned products generated by PCR were sequenced to verify the absence of introduced mutations. One day postseeding, HEK293T (A to C) or Vero cells (D) (4.5 × 105 cells/well in 6-well plates) were transfected with different combinations of expression plasmids using the Transfectin reagent (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA) using a scaled-down procedure. At 48 h posttransfection, cultures were rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline and lysed with radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (Boston BioProducts, Inc., Worcester, MA). Lysates were sonicated at 20% for 10 s with a Fisher Scientific sonic dismembrator (model 500), and debris was spun down at 14,000 × g in a microcentrifuge for 1 min. Protein concentrations were determined by bicinchoninic acid assay, following the manufacturer's instructions (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL). Proteins were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Membranes were blocked overnight at room temperature in 5% milk in phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20 (PBS-T) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO). Membranes were incubated for 1 h with mouse monoclonal antibodies (all from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) diluted in 5% milk-PBS-T. The antibodies were specific for either Myc (for detection of gB, gH, c.o. gH, and gL in panels A, B, and D), six-His (for detection of gL and c.o. gL in panel C), or β-tubulin or V5 (for detection of ORF57 in all blots and c.o. gL in panel D). After successive washings in PBS-T, blots were incubated in secondary antimouse (Santa Cruz) diluted in 5% milk in PBS-T. Blots were washed in PBS-T, and antibody binding was detected using the SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescent reagent (Pierce) and a Fuji phosphorimager. ORF57 is observed as a doublet because the transcript has multiple start sites for translation. Incubation of replicate blots or the same blot (for gB) with an anti-β-tubulin antibody was used to show equal loading. Mobility of the codon-optimized gL-V5-His protein differs slightly from that of the gL-myc-His protein because of the different epitope tag. Samples transfected with gH, c.o. gH, gL, or c.o. gL are indicated by brackets.