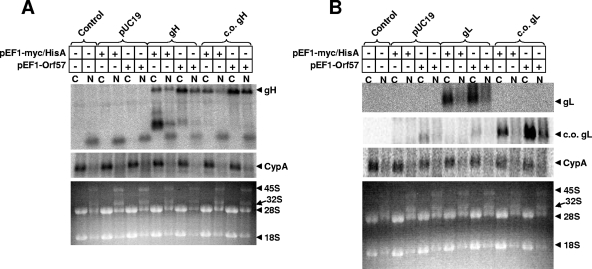
FIG. 4.
Cytoplasmic and nuclear RNA after transfection of HEK293T cells. (A) gH. (B) gL. At 48 h posttransfection, total cytoplasmic RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA), following the instructions for cytoplasmic RNA purification. Total nuclear RNA was isolated from the nuclear pellets remaining from the cytoplasmic RNA isolation procedure. The concentration of purified cytoplasmic and nuclear RNA was determined by spectrophotometry. Five micrograms of RNA was combined with formamide loading buffer (Ambion, Austin, TX), denatured at 65°C for 10 min, and loaded onto a 1% denaturing formaldehyde agarose gel containing ethidium bromide in accordance with the instructions of the NorthernMax instruction manual (Ambion). The RNA was transferred to a BrightStar-Plus membrane (Ambion) overnight and then cross-linked by UV light exposure in a commercial cross-linker (Bio-Rad). Blots were then prehybridized in UltraHyb (Ambion) for >1 h at 42°C. An end-labeled antisense oligonucleotide probe was added directly to UltraHyb and allowed to hybridize overnight at 42°C. Antisense probes were generated by 2 h of incubation of [γ-32P]ATP, antisense oligonucleotides (c-myc, 5′-CAGATCCTCTTCTGAGATGAGTTTTTGTTC-3′, or V5, 5′-ACCGAGGAGAGGGTTAGGGATAGGCTTACC-3′), and polynucleotide kinase (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA). Following this incubation, the end-labeled probes were purified using ProbeQuant G-50 Micro columns (GE Healthcare, Pittsburgh, PA). The next day, the blots were washed in triplicate with low-stringency wash solution (Ambion) for 5 min at room temperature, followed by one wash in low-stringency wash solution for 10 min at 42°C. Blots were then exposed overnight in phosphorimager cassettes, and the screens were read using a phosphorimager (BAS 2000; Fuji Photo Film Co., Tokyo, Japan). Blots were then stripped in 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, prehybridized as before, and hybridized to an antisense probe to Macaca mulatta cyclophilin A (5′-CCAAATCCTTTCTCTCCAGTGCTCAGAGC-3′) prepared as described above. Blots were rinsed, exposed to phosphorimager screens, and read as above. The lower panel for each shows the ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel. C, cytoplasmic; N, nuclear. After hybridization and exposure for detection of gH (A) or gL (B) RNA, the blot was stripped and reprobed for cyclophilin A as a control for equal RNA loading. Samples transfected with pUC19 (Invitrogen), gH, c.o. gH, gL, or c.o. gL are indicated by brackets.