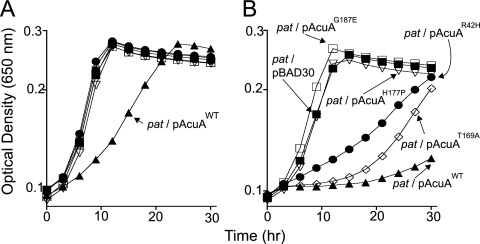
FIG. 2.
In vivo assessment of AcuAWT and variant AcuA proteins. All growth experiments were performed at least three times, and each time they were performed in triplicate. In all experiments, the standard deviation was ≤0.5. The size of the symbols obscures the error bars, but they are included in the figure. NCE minimal medium (2) containing acetate (10 mM) as a carbon and energy source was used for these experiments. (A) Behavior of the strains in the absence of l-(+)-arabinose, the inducer used to trigger the synthesis of AcuA proteins. (B) Behavior of the same strains in the presence of 500 μM l-(+)-arabinose in the medium. Filled squares, pat/pBAD30 strain (empty vector control); filled triangles, pat/pAcuAWT strain; open squares, pat/pAcuAG187E strain; open inverted triangles, pat/pAcuAH177Pstrain; circles, pat/pAcuAR42H strain; diamonds, pat/pAcuAT169A strain. For a complete description of the strain and plasmid genotypes, see Table S2 in the supplemental material. Details of the construction of plasmids and strains, the growth conditions, and medium supplements are described in the supplemental material.