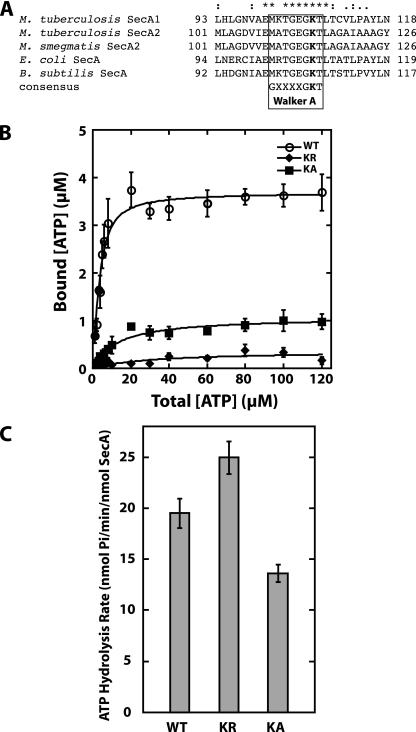
FIG. 4.
Effect of the K115R and K115A substitutions in the Walker A motif of SecA2 in vitro. (A) Alignment of Walker A motifs in SecA proteins. Sequence alignment of the highly conserved Walker A motif from mycobacterial SecA1 and SecA2 to the well-characterized SecA proteins of E. coli and B. subtilis. The conserved lysine residue that was mutated to generate SecA2(K115R) or SecA2(K115A) is shown in bold. (B) ATP binding by SecA2(K115R) (KR) and SecA2(K115A) (KA). The ATP binding was measured as described in the legend to Fig. 3. The binding data for WT SecA2 is the same as that shown in Fig. 3. (C) Endogenous ATPase activity of SecA2(K115R) and SecA2(K115A). The average rates and standard deviations of the ATP hydrolysis by each protein were determined by using the malachite green assay for determination of free inorganic phosphate, as described in the legend to Fig. 3. The WT SecA2 hydrolysis rate is the same as that shown in Fig. 3. The average rates and standard deviations from all of the experiments are shown.