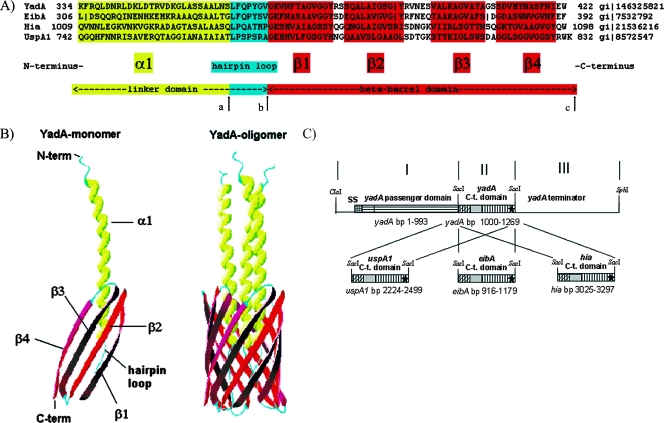
FIG. 1.
(A) Sequence alignment of the TLD monomers of YadA, EibA, Hia, and UspA1. The TLD monomer consists of two main parts: the linker domain and the beta-barrel domain. The linker domain can be separated into a proximal α1 domain, which traverses the beta-barrel domain, and a distal hairpin loop, which connects the α1 domain to the beta-barrel domain. The beta-barrel domain consists of four transmembrane antiparallel beta-sheets (β1 to β4). In this study, the YadA TLD (aa 334 to 422) was replaced with either the EibA (aa 306 to 392), Hia (aa 1009 to 1098), or UspA1 (aa 742 to 832) TLD region. Arrows mark the replaced amino acids for construction of YadA-UspA1-2 (aa 362 to 422 of YadA replaced by aa 770 to 832 of UspA1) (from arrow a to arrow c) and YadA-UspA1-3 (aa 369 to 422 of YadA replaced by aa 777 to 832 of UspA1) (from arrow b to arrow c). (B) Crystal structure model of the TLD monomer and trimer, e.g., three YadA monomers build the trimeric YadA protein (YadA oligomer). Ribbon diagrams were generated with DeepView PDB. (C) Construction scheme of the yadA chimeras. PCR fragments I, II, and III were ligated into a ClaI-SphI cut pUC-A-1 vector backbone (see Materials and Methods). SS, signaling sequence. The asterisks refer to the corresponding stop codons.