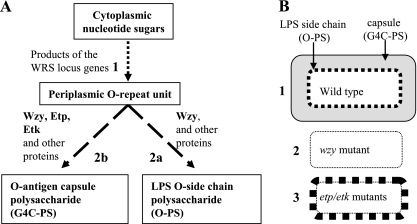
FIG. 1.
Model of G4C, O-antigen, and capsule formation and expected phenotypes of etk, etp, and wzy mutants. (A) Steps in Wzy-dependent LPS O side chain and O-antigen capsule biogenesis. In step 1, the repeat units, composed of three to five sugar residues, are synthesized in the cytoplasm and then translocated to the periplasm. This step is mediated by a large number of proteins encoded mostly in the WRS locus. Steps 2a and 2b are alternative steps. In the first, the periplasmic repeat units are polymerized by Wzy into short polymers (15 to 20 repeat units), which are then ligated to the LPS core to form O side chains. In step 2b, the repeat units are polymerized, again by Wzy, into long polymers (>100 repeat units), which are then translocated to the bacterial surface to form capsules. Etp and Etk are specifically required for step 2b, whereas Wzy is required for both 2a and 2b. The 2a and 2b pathways compete for the same O repeat units. (B) Expected phenotypes upon inactivation of etp, etk, and wzy. (Phenotype 1) Wild-type EHEC can form both LPS O side chains (thick black broken line) and O-antigen capsules (gray zone around the bacteria), both indicated by arrows. (Phenotype 2) Mutants deficient in repeat unit synthesis or polymerization (wzy mutant), are expected to lack both LPS O side chains and O capsules (the thin dotted line represents the smooth outer membranes). (Phenotype 3) etk or etp mutants are expected to be deficient in O-capsule formation but to exhibit enhanced LPS O side chain formation (represented by the thick black broken line) since pathway 2b is no longer competing with pathway 2a (panel A) (32).