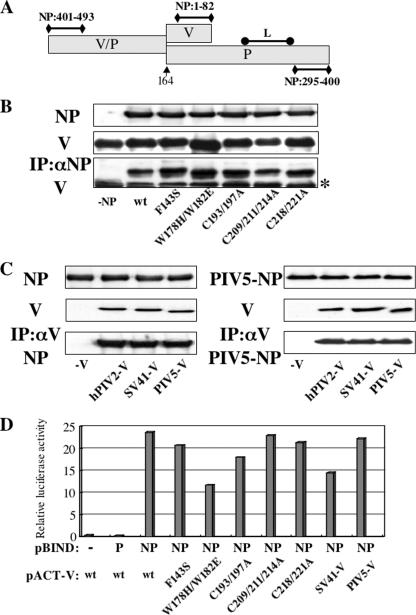
FIG. 6.
Analysis of interactions between NP and V proteins by immunoprecipitation. (A) Schematic diagram of P/V regions required for binding to NP and L proteins previously identified. The numbers show amino acid residues on the NP protein. The arrow marks the editing site. (B) BSR T7/5 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing hPIV2 NP and mutant hPIV2 V proteins. At 48 hpt, the cell extracts were either analyzed directly by Western blot analysis (anti-NP; upper panel, anti-V; middle panel) or immunoprecipitated with anti-NP before Western blot analysis (anti-V; lower panel). The asterisk on the right indicates the immunoglobulin light chain. (C) BSR T7/5 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing hPIV2 (left panel) or PIV5 (right panel) NP and rubulavirus V proteins. At 48 hpt, the cell extracts were either analyzed directly by Western blot analysis (anti-NP, upper panel; anti-V and PIV5-V, middle panel) or immunoprecipitated with anti-V or PIV5-V before Western blot analysis (anti-NP, lower panel). (D) Mammalian two-hybrid analysis for NP and various V proteins. COS cells were cotransfected with pBIND and pACT plamids together with luciferase reporter plasmid. After 48 h, the cells were harvested and assayed by dual-luciferase reporter assay system. The pACT-V wt and mutant constructs refer to the hPIV2 V proteins; those of the other virus V proteins are specified.