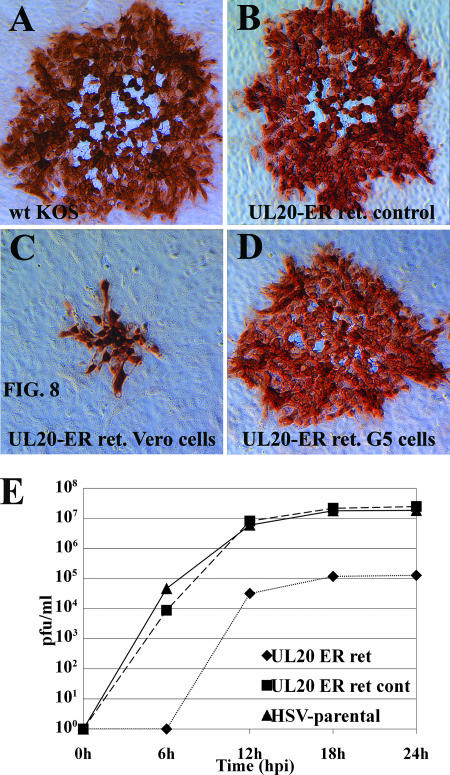
FIG. 8.
Retention of UL20p within the ER blocks efficient plaque formation and virus cell-to-cell spread. Confluent Vero (A to C) or UL20-complementing G5 (D) cell monolayers were infected with either parental wild-type KOS virus (A), UL20p ER retention control virus (B), or UL20p ER retention virus (C and D) at an MOI of 0.001, and viral plaques were visualized by immunohistochemistry at 48 hpi. (E) Comparison of replication kinetics of parental wild-type, UL20 ER retention control, and UL20 ER retention viruses.