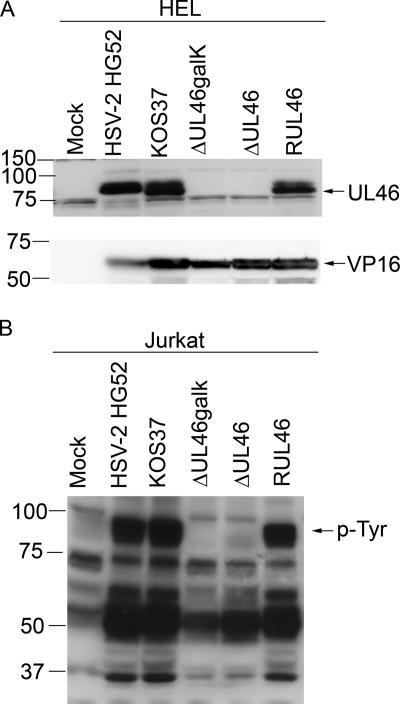
FIG. 4.
Analysis of UL46 and tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in cells infected with UL46 mutants. (A). HEL fibroblasts were either mock infected or infected with wild-type HSV (HSV-2 HG52, HSV-1 KOS-37), the UL46-null viruses (ΔUL46galk, ΔUL46), or the UL46 repair virus (RUL46). Cell extracts prepared 16 h postinfection were then analyzed by Western blotting using a rabbit polyclonal antiserum directed against HSV-2 strain 186 UL46 (top panel) and monoclonal antibody LP1, directed against VP16 (bottom panel). (B) Jurkat cells were exposed as before to HEL fibroblasts that had been either mock infected or infected by wild-type HSV (HSV-2 HG52, HSV-1 KOS-37), a UL46-null virus (ΔUL46galk, ΔUL46), or the UL46 repair virus (RUL46). The Jurkat cells were then removed, and extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with an antiphosphotyrosine antibody. The mobility of the prominent 90-kDa tyrosine-phosphorylated protein is indicated (p-Tyr).