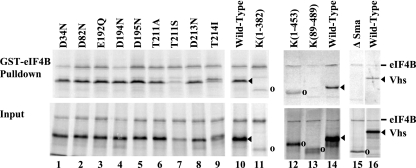
FIG. 5.
Binding of wild-type HSV-1(KOS) and mutant Vhs polypeptides to GST-eIF4B. [35S]methionine-labeled HSV-1(KOS) and mutant Vhs polypeptides were produced by in vitro transcription and translation, mixed with [35S]methionine-labeled in vitro-translated eIF4B, and analyzed for the ability to bind GST-eIF4B (14, 17, 18). Proteins that bound to GST-eIF4B were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography in the upper panel (GST-eIF4B Pulldown), while aliquots of the input in vitro-translated material are shown in the lower panel (Input). The wild-type HSV-1(KOS) and mutant Vhs polypeptides are indicated at the top of each lane. Their structures are diagrammed in Fig. 6. All binding reactions were performed in the same experiment, but lanes 1 through 9 were run on one gel, lanes 10 and 11 on another, lanes 12 through 14 on a third gel, and lanes 15 and 16 on a fourth. The gels were not run for precisely the same length of time, which is why the electrophoretic mobility of wild-type Vhs, relative to eIF4B, was not the same for the different gels. The location of the wild-type Vhs protein is indicated by filled arrowheads to the right of lanes 10, 14, and 16. The locations of mutant Vhs polypeptides that are not full length are shown by open circles to the right of lanes 11 to 13 and 15.