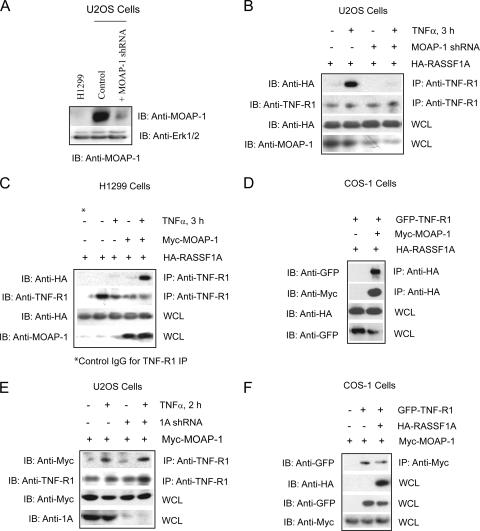
FIG. 1.
MOAP-1 is required for the association of RASSF1A with TNF-R1. (A) Expression of endogenous MOAP-1 in H1299 cells, control U2OS cells, or U2OS cells containing MOAP-1 shRNA. (B) Pooled U20S cells expressing control (−) or MOAP-1 shRNA (+) were used to determine RASSF1A association with TNF-R1. The association of ectopically expressed HA-RASSF1A with endogenous TNF-R1 was recovered by immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-TNF-R1 antibody followed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. (C) HA-RASSF1A association with endogenous TNF-R1 was carried out as in panel B but in H1299 cells without (−) or with (+) ectopically expressed Myc-MOAP-1. Control antibodies (control immunoglobulin G) did not reveal immunoprecipitation of TNF-R1 or HA-RASSF1A (data not shown, but see Fig. 6C for an example). (D) RASSF1A, MOAP-1, and TNF-R1 were ectopically expressed in COS-1 cells, and proteins associated with RASSF1A were recovered by immunoprecipitation with an anti-HA antibody followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) Pooled U20S cells expressing control (−) or RASSF1A (1A) shRNA (+) as previously described (2) were used to determine MOAP-1 association with endogenous TNF-R1 as outlined in panel B. (F) MOAP-1, RASSF1A, and TNF-R1 were ectopically expressed in COS-1 cells, and proteins associated with MOAP-1 were recovered by immunoprecipitation with an anti-Myc antibody followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.