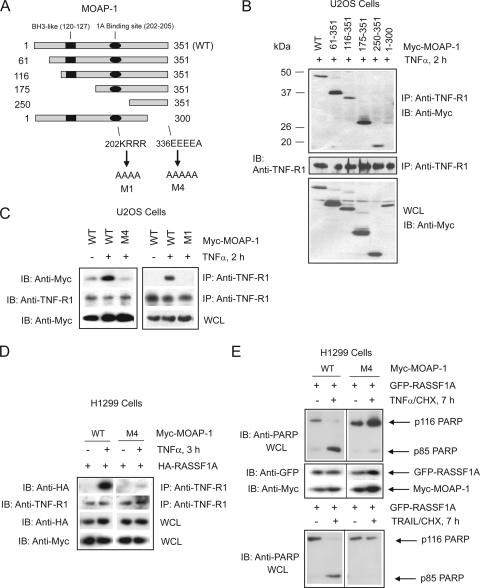
FIG. 4.
Location of MOAP-1 residues important for TNF-R1 association. (A) Schematic of MOAP-1 mutants used in panel B indicating the locations of critical residues and domains. Numbers indicate amino acid location, and arrows denote amino acid changes. MOAP-1 deletion mutants (B) or point mutants (C) were ectopically expressed, and proteins associated with endogenous TNF-R1 were recovered by immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-TNF-R1 antibodies followed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. All lanes were stimulated with TNF-α for 2 h. WT, wild type. (D) H1299 stable cells were generated containing either wild-type MOAP-1 or MOAP-1 mutant M4, which lacked the ability to associate with endogenous TNF-R1. HA-RASSF1A was ectopically expressed, and association with endogenous TNF-R1 was recovered by immunoprecipitation with anti-TNF-R1 antibodies followed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) H1299 stable cells were generated as in panel D, and GFP-RASSF1A was ectopically expressed, stimulated with TNF-α (top) or TRAIL (bottom), lysed in RIPA buffer, and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.