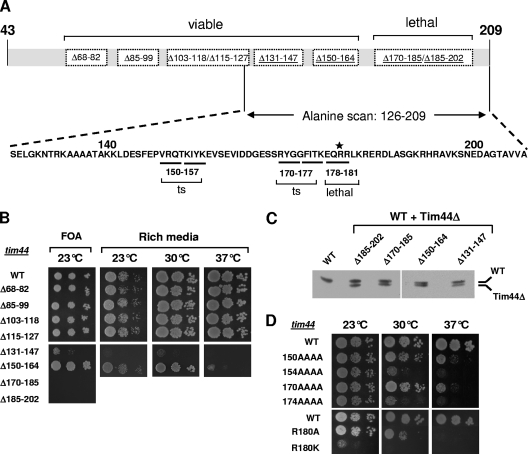
FIG. 2.
Mutational analysis of TIM44. (A) Overview of the phenotypes of tim44 mutants. (Top) Eight deletion mutants lacking 12 to 17 amino acids within the interval of residues 68 to 202 of Tim44 (dotted rectangles). Deletion mutations causing phenotypic effects are underlined (see panel B). (Bottom) Alanine scanning of the segment containing residues 126 to 209. Twenty-one quadruple mutants substituting four alanines for four consecutive native residues were constructed. Amino acid substitutions leading to growth defects are underlined. Residue R180, which is critical for Tim44's in vivo function, is labeled with an asterisk. ts: temperature sensitive. (B) Growth phenotypes of tim44Δ strains carrying deletions within the coding sequence for the N-terminal segment of Tim44. Tenfold serial dilutions of cells were plated on the indicated medium. (Left) Medium containing 5-FOA. tim44Δ strains expressing the indicated plasmid-encoded mutant and wild-type (WT) TIM44 genes were expressed at 23°C for 4 days. (Right) Strains recovered from plating on 5-FOA were spotted onto rich glucose-based medium (rich) and incubated for 3 days (23°C) or 2 days (30°C and 37°C). (C) Protein expression. Cell extracts of tim44Δ strains expressing both the indicated mutant and WT TIM44 genes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using Tim44-specific antibodies. Cells harboring both WT and mutant TIM44 genes on different plasmids were grown at 23°C in minimal medium to select for the presence of both plasmids. See Materials and Methods for details. (D) Growth phenotypes of TIM44 amino acid substitution mutants. Cells were plated onto rich medium and incubated at the indicated temperatures for 3 days.