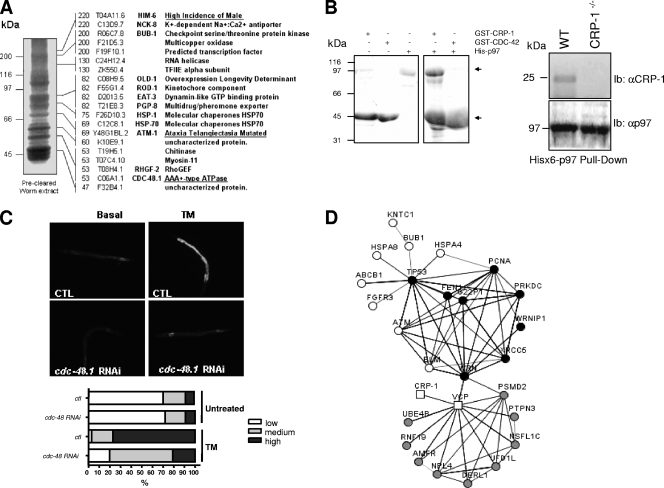
FIG. 4.
CRP-1 interacts with a protein complex which includes CDC-48.1 and ATM-1. (A) SDS-PAGE of the GST-CRP-1 pull-down performed on precleared worm lysate, followed by mass spectrometry analysis (right). Peptides identified were annotated using the WormBase (http://www.wormbase.org/) sequence name as well as the Caenorhabditis Genetic Center (http://www.cbs.umn.edu/CGC/) three-letter name. (B, left) GST pull-down using GST-CRP-1 or GST-CDC-42 and mouse His6-p97/VCP/CDC-48 recombinant proteins expressed in bacteria and resolved on SDS-PAGE gel stained with Coomassie blue R250. (Right) His6-p97/VCP/CDC-48 pull-down was performed on wild-type (WT) (N2) or crp-1−/− total worm extract followed by immunoblot analysis using anti (α)-CRP-1 antibodies (HyperOmics Farma, Inc.) or anti-p97 antibodies. (C) Transcriptional regulation of pckb-2::gfp reporter by cdc-48. pckb-2::gfp transgenic worms were subjected or not to cdc-48.1 RNAi as described in Materials and Methods. Following exposure to TM, pckb-2::gfp activation was visualized and quantified using fluorescence microscopy. (D) STRING network representation of the known and predicted interactions between proteins identified by mass spectrometry (white), VCP (p97/VCP/CDC-48) first-interacting proteins (gray), and ATM-1 first-interacting proteins (black). The edges are representative of the various interaction types available through STRING. Circles and squares are indicative of human and C. elegans genes, respectively (see also Table S3 in the supplemental material).