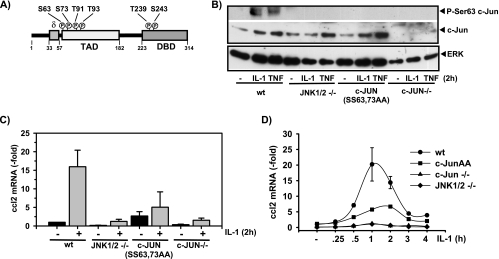
FIG. 1.
JNK- and c-Jun-dependent ccl2 mRNA expression in genetically altered mouse fibroblasts. (A) Schematic representation of the c-Jun structure, indicating the N-terminal transactivation domain (TAD), the C-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD), and the JNK-binding domain (δ). Each circled “P” indicates a phosphorylation site. (B) Wild-type (wt) embryonic fibroblast cell lines, cells lacking JNK1 and JNK2 genes (JNK1/2 −/−) or c-Jun (c-Jun−/−), or cells that were isolated from mice carrying a c-Jun allele mutated in two of the four JNK phosphoacceptor sites (c-Jun SS63/73AA) were kept in low-concentration (0.1%) serum for 48 h. Thereafter, cells were treated for 2 h with 10 ng/ml IL-1α or were left untreated. Phosphorylation and expression of c-Jun were analyzed by Western blotting of whole-cell extracts. ERK antibodies were used to control for protein loading. (C) The cells described for panel B were kept in low-concentration (0.1%) serum for 48 h. Thereafter, they were treated for 2 h with IL-1α (10 ng/ml). ccl2 mRNA expression was determined by TaqMan real-time PCR using total RNA. The values shown represent mean ccl2 expression ± the standard errors of the means of the results from three independent experiments relative to the unstimulated wild-type control cell results. (D) ccl2 mRNA expression was determined as described for panel C for cells kept in low-concentration serum that were treated for the indicated times with IL-1α (10 ng/ml). Expression of ccl2 was analyzed as described for panel C. The values shown represent mean ccl2 expression ± the standard errors of the means of the results from two independent experiments relative to the unstimulated wild-type control cell results.