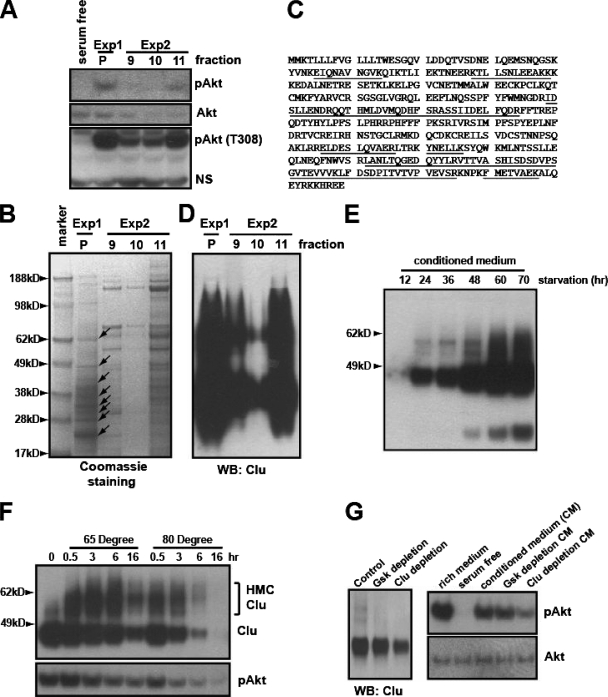
FIG. 4.
Biochemical purification identified clusterin as a protein associated with the PI3K-Akt-activating activity. (A) The active fractions eluted from the High S column from two independent purification experiments (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material) were mixed (1:1) with serum-free medium. After heat treatment, their ability to phosphorylate S473 and T308 of Akt was assayed in NB4 cells. Exp1 and Exp2 indicate two independent purification experiments. P indicates the pooled activity from the first purification. NS indicates a nonspecific band. (B) The corresponding fractions were concentrated with a Centriprep 10K column. Proteins were resolved on a NuPAGE 4 to 12% gel stained with Coomassie blue. Arrows indicate the protein bands analyzed by MALDI mass spectrometry. (C) Human clusterin peptides identified by MALDI analysis are underlined. (D) Western blotting (WB) of the corresponding fractions, using C-terminal-specific monoclonal clusterin antibody. (E) Serum-free CM from HeLa cells collected at the indicated time points was analyzed for clusterin. (F) CM from HeLa cells was heat treated for the indicated times, and proteins were analyzed with the C-terminal-specific clusterin antibody. The bracket indicates the high-molecular-weight complexes induced by heat treatment (top). Akt-activating activity of the corresponding CM was tested in NB4 cells (bottom). (G) CM was immunodepleted with the protein G/A beads alone (control), the control antibody (monoclonal anti-GSK), or the C-terminal-specific clusterin antibody. The supernatant was analyzed for clusterin (at left). Their abilities to activate Akt were tested in NB4 cells (at right).