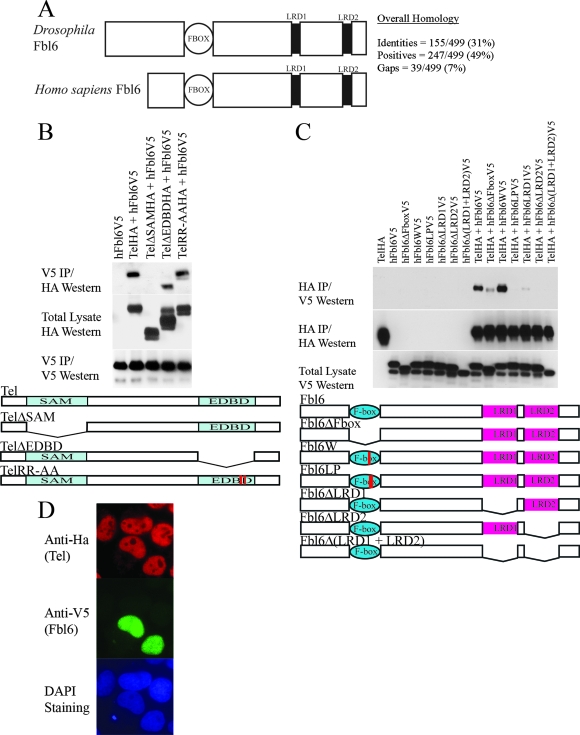
FIG. 1.
(A) Schematic representation of human and Drosophila Fbl6 proteins. Fbl6 is characterized by a conserved, N-terminal F-box domain (1) that is 40 to 50 amino acids long. Two other blocks of conserved sequences, which have previously been defined as leucine-rich regions (LRD1 and LRD2), are represented by black rectangles (4). The alignments of the primary amino acid sequences can be found in Fig. S1 in the supplemental material. (B) The SAM domain of Tel is needed for association with Fbl6 in cells. HA epitope-tagged wild-type Tel, TelΔSAM, TelΔEDBD, and Tel harboring substitutions of alanine for arginine in the Ets DNA-binding motif (KMSRALRHYYK) were each coexpressed with V5 epitope-tagged human Fbl6 in 293T cells. Fbl6 complexes were immunopurified from cell lysates using an antibody directed against the V5 epitope, and associated Tel proteins were detected using an antibody directed against the HA epitope. (C) The LRDs of Fbl6 and an intact F-box domain are essential for interacting with Tel. V5 epitope-tagged full-length Fbl6 or the indicated Fbl6 mutants were coexpressed with Tel in 293T cells. Tel complexes were immunopurified from cell lysates by using an antibody directed against the HA epitope, and associated Fbl6 proteins were detected using an antibody directed against the V5 epitope. Fbl6ΔFbox contains a deletion of the F-box domain. Fbl6W and Fbl6LP have point mutations that have been shown to disrupt the F-box domain (37). Fbl6ΔLRD1 and Fbl6ΔLRD2 harbor deletions of the LRD1 and LRD2 sequences, respectively. Fbl6Δ(LRD1 + LRD2) has a deletion of both LRD1 and LRD2. h, human. (D) Fbl6 and Tel are colocalized in the nucleus. Cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and proteins detected with the indicated antibodies. DAPI, 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole.