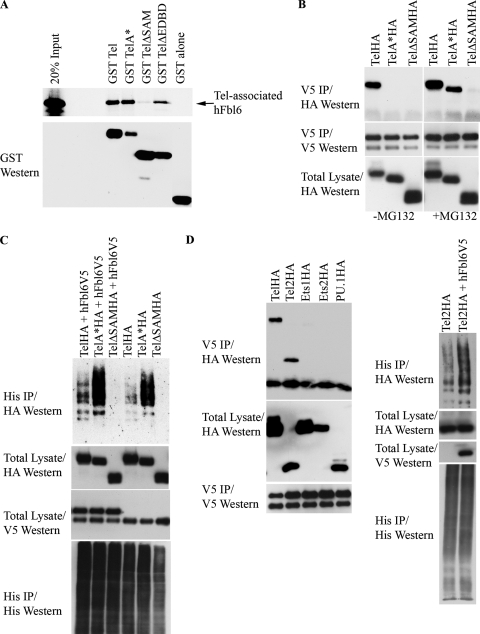
FIG. 3.
(A) Fbl6 binds efficiently with Tel monomers in vitro. Fusions were made between GST and either full-length wild-type Tel, full-length Tel harboring mutations that disrupt the SAM domain (TelΔSAM and TelA*), or TelΔEDBD (see text for details). 35S-labeled Fbl6 was produced by in vitro translation in reticulocyte lysates and assessed for binding to GST-Tel. (B) Inhibition of proteasome function stabilizes the interaction between Tel monomers and Fbl6 in cells. Cells were cotransfected with the indicated Tel constructs along with V5 epitope-tagged Fbl6. Following incubation with (+) or without (−) MG132, Fbl6 complexes were immunopurified from cell lysates by using an antibody directed against the V5 epitope, and the associated Tel protein was detected using an antibody directed against the HA epitope. (C) Tel monomers can bind with Fbl6 and are efficiently ubiquitinated; their ubiquitination is augmented by Fbl6. U2OS cells were cotransfected with the indicated constructs together with His epitope-tagged ubiquitin, and a ubiquitination assay was performed. (D) Fbl6 interacts with Tel2 and stimulates its ubiquitination. HA epitope-tagged versions of the indicated Ets transcription factors were coexpressed with or without Fbl6. Fbl6 complexes were immunopurified from cell lysates using an antibody directed against the V5 epitope, and associated Ets proteins were detected using an antibody directed against the HA epitope. For the ubiquitination assay, cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and processed as described in the legend to Fig. 2A. Western, Western blotting; IP, immunoprecipitation; h, human.