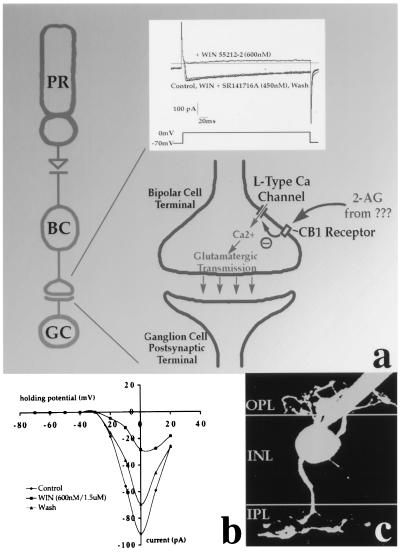
Figure 5.
Activation of CB1 receptors by WIN 55212–2 inhibits the voltage-gated calcium channel currents in retinal bipolar cell axon terminals. Recordings were made in the presence of tetraethylammonium (40 mM) and BaCl2 (10 mM). (a) Traces represent L-type Ca2+ current in response to a depolarizing voltage step from −70 mV to +10 mV under control conditions, in the presence of CB1 agonist WIN 55212–2 [600 nM (n = 4) or 1.5 μM (n = 3)], with WIN 55212–2 and the selective CB1 antagonist SR141716A (450 nM-1 μM), and after wash. Shown is a hypothetical model cannabinoid receptor effect on glutamate release from bipolar cells via inhibition of L-type calcium currents. (b) Current-voltage relation shows a 70% inhibition of peak current by cannabinoids. Mean peak amplitude (at 0 mV, n = 7) is −92pA. Mean peak amplitude with WIN is −28pA. Treatment with CB1 antagonist or washing both restored currents. (c) Example of bipolar cell filled with fluorescent calcein dye during recording. Boundaries of the synaptic layers were determined by concurrent imaging with differential interference contrast optics.