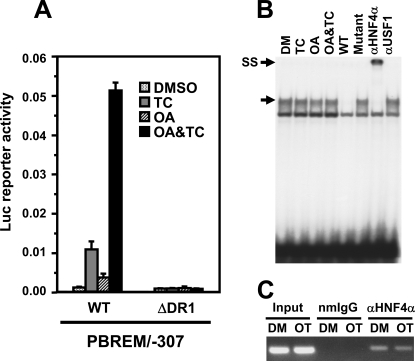
FIGURE 3.
HNF4α as a constitutive factor regulating OAREKI. A, transient transfection assays to show HNF4α activity. Ym17 cells were co-transfected by PBREM/-307 (WT) or its DR1 deletion mutant (ΔDR1) and phRL-SV40 into Ym17 cells and were subsequently treated with Me2SO (DMSO), 250 nm TCPOBOP (TC), 10 nm OA, or TCPOBOP plus OA (OA&TC). Reporter activity was calculated by dividing firefly luciferase activity with Renilla luciferase activity. B, gel shift assays to show binding of HNF4α to DR1 motif within OAREKI. Double-stranded 32P-end-labeled DR1 probe (–229/–217) was incubated with nuclear extracts (2 μg) prepared from Ym17 cells treated with Me2SO (DM), 250 nm TCPOBOP, 10 nm OA, or OA plus TCPOBOP for 36 h. For competition assays, a 50-fold excess of unlabeled DR1 probe (–229/–217, wild type) or its mutated probe (Mutant) was added into the reaction mixture. Anti-HNF4α antibody (αHNF4α) or unrelated antibody (αUSF1) was used for supershift assays. The arrows indicate specific shifted band and supershifted band (SS). C, ChIP assays to show HNF4α interacts with CYP2B6 promoter regardless of drug treatment. Cross-linked chromatin-protein complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-HNF4α (αHNF4α) or normal mouse IgG (nmIgG), and PCR amplicon (–338 to –99) was resolved on a 1.5%, agarose gel.