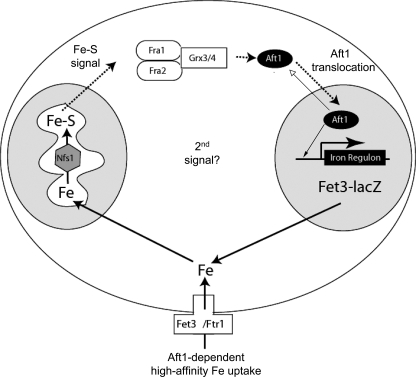
FIGURE 11.
Model for the role of Fra1-Fra2 in the regulation of Aft1 transcriptional activity. In the absence of mitochondrial Fe-S cluster synthesis, Aft1 translocates into the nucleus and induces the transcription of its target genes, such as the plasma membrane high affinity iron permease complex Fet3-Ftr1. The signal from the mitochondria is not known, but it is interpreted in the cytosol by a protein complex consisting of the Fra1-Fra2 proteins with Grx3-Grx4. This complex inhibits the translocation of Aft1 into the nucleus. Our data suggest that Aft1 does not bind to the Fra1-Fra2 complex, indicating that there is not a direct physical interaction between the two. The Fra1-Fra2-Grx complex may affect sulfhydryl status on Aft1 or on an Aft1-interacting protein. Low iron conditions reduce the rate of Fe-S cluster synthesis, resulting in a signal through the Fra1-Fra2-Grx complex and in Aft1 translocating to the nucleus, where it occupies the FET3 promoter. Further decreases in cytosolic iron may affect the amount of Aft1 bound to the promoter, leading to an increase in transcriptional activation.