FIGURE 3.
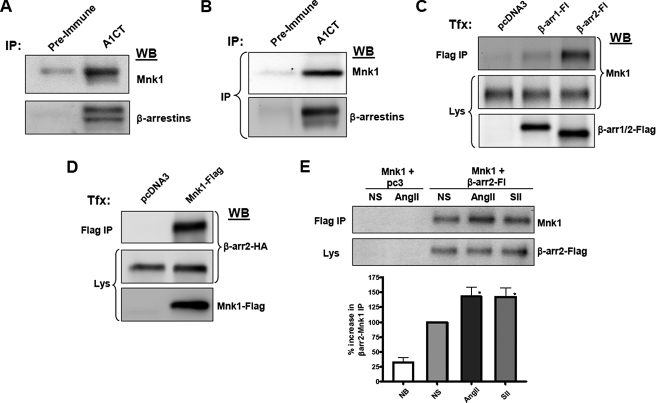
β-Arrestins physically interact with Mnk1 in vivo and in vitro. A, HeLa cells were lysed and immunoprecipitated with aβ-arrestin-specific antibody (A1CT) or pre-immune serum from the same rabbit. Western blots were performed with antibodies to detect human Mnk1 (upper panel) or a monoclonal antibody to detect immunoprecipitated β-arrestins (lower panel). B, spleens were harvested from C57Black6 mice and immunoprecipitated with A1CT or pre-immune serum. Western blots were performed with an antibody for murine Mnk1 or with a monoclonal β-arrestin antibody. C, Mnk1 and β-arrestins interact in transfected cells. HEK-293 cells stably expressing Mnk1 were transfected with empty vector or plasmids expressing β-arrestin1-FLAG or β-arrestin2-FLAG and immunoprecipitated with a FLAG-M2 antibody. Western blots were performed for Mnk1. D, reciprocal IP. Empty vector or Mnk1-FLAG expression plasmid was cotransfected with a β-arrestin2-HA expression plasmid. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with a FLAG-M2 antibody, and HA Western blots were performed to detect β-arrestin2. All results shown are representative of three similar experiments. E, agonist effect on IP. Similar methods as in C, except cells were serum-starved and stimulated for 30 min with AngII or SII. Results of six experiments ± S.E. are shown in the graph. NB, no bait control, NS, nonstimulated. NB versus NS (p < 0.05), NS versus AngII (*, p < 0.05) or SII (*, p < 0.05).