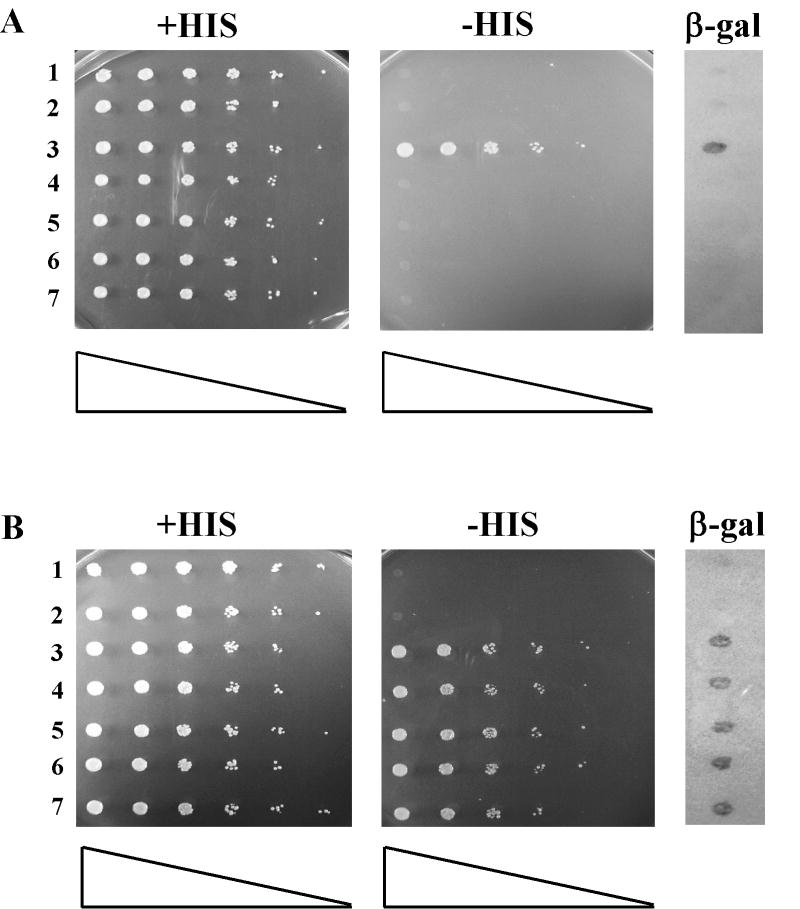
Figure 3.
The FF->AA mutation prevents Exo1p from interacting with Mlh1p, but not Msh2p by yeast two-hybrid. Strains with designated bait-prey sets were grown in nonselective media (-TRP -URA) to saturation, serially diluted (1:5), spotted on the indicated plates using a 48-prong replicator and then incubated at 30 °C for 3 days. Strains were assayed for β-gal activity by lift assays as described in the Materials and Methods. Growth on –HIS plates and blue color development on the β -gal assay indicates interaction between the bait and prey fusion proteins. (A) Mlh1p-LexAp bait and Exo1p-Gad4p prey combinations demonstrate that the exo1-FF447AA mutation prevents Exo1p-Gad4p interaction with Mlh1p-LexAp. Lanes: 1, pBTM (empty bait control) + pGAD (empty prey control); 2, pBTM-MLH1 + pGAD; 3, pBTM-MLH1 + pGAD-EXO1; 4, pBTM-MLH1 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 1; 5, pBTM-MLH1 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 5; 6, pBTM-MLH1 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 6; and 7, pBTM-MLH1 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 10. (B) Msh2p-LexAp bait and Exo1p-Gad4p prey combinations demonstrate that the exo1-FF447AA mutation does not prevent Exo1p-Gad4p interaction with Msh2p-LexAp. Lanes: 1, pBTM (control) + pGAD (control); 2, pBTM-MSH2 + pGAD; 3, pBTM- MSH2 + pGAD-EXO1; 4, pBTM- MSH2 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 1; 5, pBTM- MSH2 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 5; 6, pBTM- MSH2 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 6; and 7, pBTM- MSH2 + pGAD-exo1-FF447AA # 10. Clones pGAD-exo1-FF447AA #1, 5, 6 & 10 represent four independently generated “prey” constructs.