Figure 1.
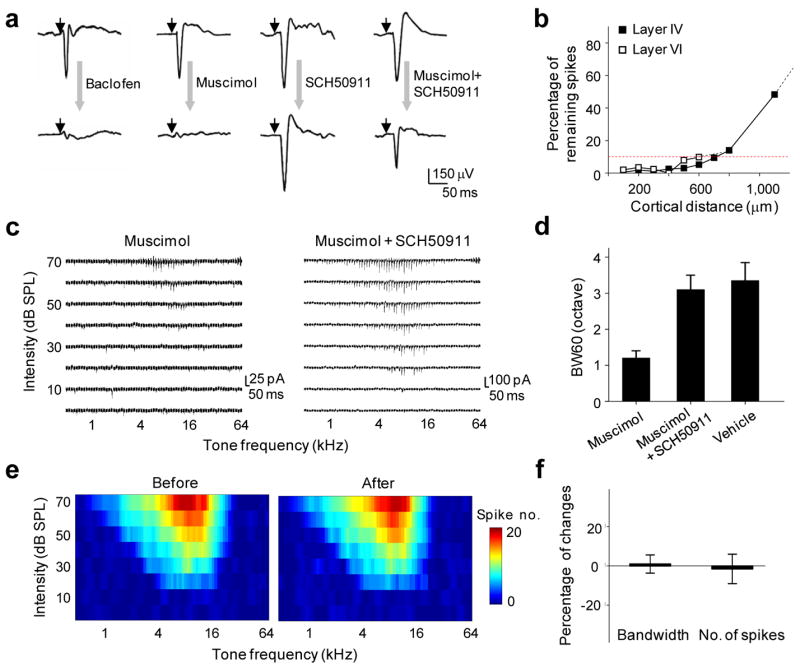
Specific silencing of local intracortical connections with a cocktail pharmacological method. (a) Tone-evoked field potentials recorded in A1 before (top) and after (bottom) cortical injection of muscimol (1 mM), baclofen (1 mM), SCH50911 (1.5mM) or a cocktail of muscimol (1 mM) and SCH50911 (1.5 mM). Small arrow marks the onset of tone stimulus. (b) Effective blocking of cortical spikes by the muscimol and SCH50911 (4mM: 6mM) cocktail in both layer 4 and layer 6 within a horizontal distance of 500 μm from the injection site (see Methods). Multi-unit tone-evoked spikes were detected by extracellular recordings. Red dot line indicates 90% reduction in spike count. (c) Example excitatory synaptic TRFs of A1 neurons obtained shortly after muscimol injection (left) and cocktail injection (right). Each small trace represents the response (recorded at −70mV) to a tone of a particular frequency and intensity. (d) Average bandwidth of synaptic TRF measured at 60dB (BW60) in A1 injected with muscimol, cocktail, or vehicle solution (ACSF). Bar is s.d. (e) Spike TRF (average of four repetitions) for a recording site in the MGBv before and after cortical injection of the cocktail. Color represents the number of spikes evoked by a tone stimulus. (f) Percentage change in the bandwidth and spike count for tone evoked spikes (measured at 60 dB) in the MGBv before and after cortical cocktail application (n = 6 sites). Bar = s.d.
