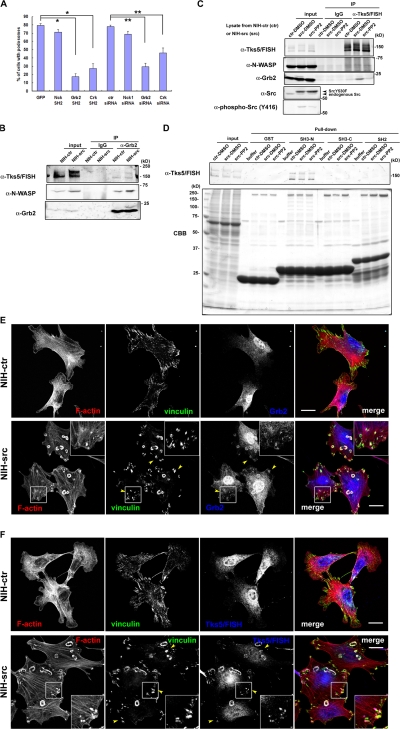
Figure 3.
Tks5/FISH binds with Grb2 in an Src-dependent manner. (A) Myc-tagged SH2 domain of Nck, Grb2, or Crk was expressed in NIH-src cells, and the cells with podosomes were counted. For RNAi experiments, the NIH-src cells were transfected with each siRNA. The percentage of transfected cells that developed podosomes was calculated. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three different measurements. *, P < 0.002 by Student's t test compared with GFP. **, P < 0.001 by Student's t test compared with control siRNA. A minimum of 50 cells were counted for each determination. (B and C) Immunoprecipitations with anti-Grb2 (B) or anti-Tks5/FISH (C) were performed as described in Materials and methods. Western blot was performed by cropping the original membrane according to the molecular weight of Tks5/FISH, N-WASP, and Grb2, respectively, to detect them simultaneously. The bound proteins were analyzed by using anti-Tks5/FISH, anti-N-WASP, or anti-Grb2 antibody. (D) NIH-ctr or NIH-src cell lysates were mixed with the GST-SH3 or GST-SH2 domains of Grb2 immobilized on beads; the bound proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and Tks5/FISH was detected by using anti-Tks5/FISH antibody. (E and F) Grb2 (E) or Tks5/FISH (F) (blue) in NIH-ctr cells and NIH-src cells was stained with anti-Grb2 (rabbit polyclonal) or anti-Tks5/FISH, respectively. They were co-stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (red) and anti-vinculin (green) as an adhesion marker. Arrowheads indicate the FA-related adhesions of NIH-src cells where Grb2 or Tks5/FISH accumulated. The regions outlined by boxes are examples of FA-related adhesions magnified twofold. Bars, 20 μm.