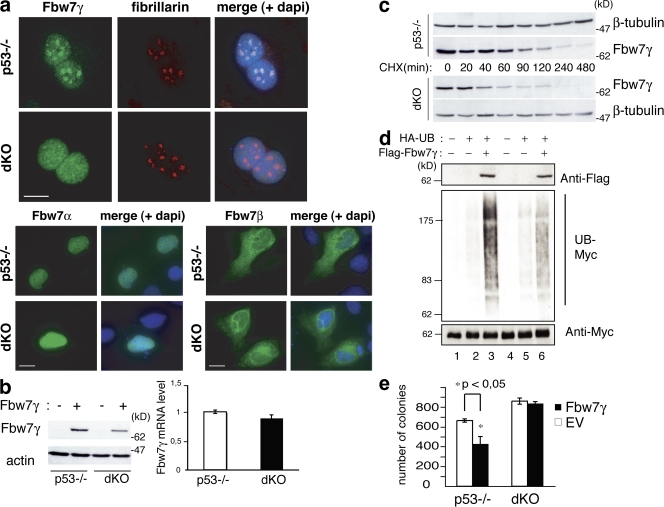
Figure 3.
NPM is required Fbw7γ nucleolar localization and stability. (a) IF analysis of Fbw7γ (top), Fbw7α (bottom left), and Fbw7β (bottom right) localization in p53−/− and dKO MEFs transiently transfected with the corresponding flag-Fbw7 constructs (green staining). Anti-fibrillarin staining (red) is shown as a marker for nucleoli. Bars, 10 μm. (b, left) WB analysis in p53−/− and dKO MEFs infected with retroviruses expressing HA-Fbw7γ (+) or control retroviruses (−) as indicated. (right) Fbw7γ mRNA levels in p53−/− and dKO MEFs. (c) HA-Fbw7γ protein stability in p53−/− and dKO MEFs. Cells were treated with CHX and harvested at the indicated time points. (d) Effects of Fbw7γ expression on Myc ubiquitination in p53−/− and dKO cells. p53−/− (lanes 1–3) and dKO (lanes 4–6) MEFs were transfected with expression vectors for HA-tagged ubiquitin and flag-tagged Fbw7γ, as indicated. Cell lysates were IPed with an anti-Myc antibody and blotted with anti-HA (to identify ubiquitinated myc; UB-myc) and anti-Myc (as control) antibodies. Levels of flag-Fbw7γ in the input were analyzed with an anti-flag antibody. (e) Methylcellulose colony assay of p53−/− and dKO MEFs expressing Myc-ER protein and infected with control (EV) or HA-Fbw7γ–expressing retroviruses. 4-OHT was added every 3 d; colonies were counted after 15 d. Data represent the mean of three determinations ± SEM. *, P < 0.045.